Association of atherogenic index of plasma with early-onset post-stroke depression: a prospective study
- PMID: 40787681
- PMCID: PMC12331589
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1563289
Association of atherogenic index of plasma with early-onset post-stroke depression: a prospective study
Abstract
Background: The atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) is a newly developed marker of lipids that has strong prognostic value in people with cardiovascular disease. Nevertheless, few studies concern the relationship between AIP and early-onset post-stroke depression (PSD).
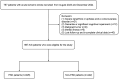
Methods: After two weeks of acute ischemic stroke (AIS), early-onset PSD was identified. The Hamilton Depression Scale-17 items (HAMD-17) was used to assess the severity of depression. Patients with HAMD-17 scores ≥7 were divided into an early-onset PSD group. Spearman rank correlation analysis was employed to evaluate the associations between AIP and HAMD scores across all patients. Logistic regression analysis was conducted to investigate the associations between the AIP and early-onset PSD. Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis was used to determine the predictive value of the AIP for early-onset PSD.
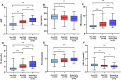
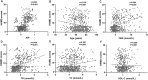
Results: Among the 667 recruited patients, a total of 225 (33.73%) patients were diagnosed with early-onset PSD. The AIP showed a positive correlation with the HAMD-17 scores (r=0.567, P<0.001). A binary logistic regression model demonstrated that the AIP (odds ratio [OR], 1.843; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.650-2.558, P<0.001) was an independent factor for early-onset PSD. The AIP for early-onset PSD had an area under the curve (AUC) value of 0.785.
Conclusions: Our study indicates that the AIP may serve as an independent risk factor for early-onset PSD, offering insights for the prevention and management of prognosis in affected patients.
Keywords: abnormal lipid metabolism; acute ischemic stroke; atherogenic index of plasma; depression; post-stroke depression.
Copyright © 2025 Deng, Song, He, Zhao, Xu, Feng, Chen, Tong, Fei, Wang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the Atherogenic Index of Plasma in the Prognostic Value of Ischemic Heart Failure Post-Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jun 30;26(6):33470. doi: 10.31083/RCM33470. eCollection 2025 Jun. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40630430 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the atherogenic index of plasma and risk of large-artery atherosclerotic ischemic stroke.Front Neurol. 2025 Aug 6;16:1529628. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1529628. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40843262 Free PMC article.
-
TyG-BMI as a predictor of ischemic stroke over 10 years in middle-aged and older adults: findings from the China cardiometabolic disease and cancer cohort (4C) study.Front Neurol. 2025 Jul 2;16:1609853. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1609853. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40672456 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

