Diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumor (DLGNT): a comprehensive clinical and molecular analysis
- PMID: 40788548
- PMCID: PMC12339613
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-025-02924-0
Diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumor (DLGNT): a comprehensive clinical and molecular analysis
Abstract
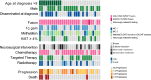
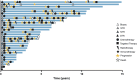
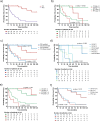
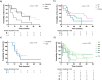
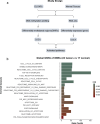
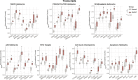
Diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumors (DLGNTs) are rare, and optimal treatment remains undefined. We aim to comprehensively characterize their clinical and molecular features, offering granular insights into presentations and therapies to elucidate prognostic factors and therapeutic targets. Histologic, molecular, and clinical data of 30 patients with DLGNT were analyzed. Median age at diagnosis was 7.5 years (range: 0.9-20 years). Disease was localized at diagnosis in 16 patients (53.3%), predominantly in the spinal cord (14/16, 87.5%). KIAA1549::BRAF fusion occurred in 27 (96.4%) of 28 patients. DNA methylation profiling of 23 tumors classified 4 (17.4%) as DLGNT MC-1, 3 (13.0%) as DLGNT MC-2, and 16 (69.6%) as DLGNT, but not to a specific subclass. Median follow-up was 57.5 months. Most patients (90.0%) received adjuvant therapy. Chemotherapy was the first-line adjuvant therapy in 19 patients (70.4%); targeted therapy in 5 patients (18.5%), and radiotherapy in 2 patients (7.4%). Median progression-free survival (PFS) after first chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiotherapy was 44 (1-77) months, 18 (4-39) months, and 16.5 (9-23) months, respectively. Five-year PFS was 15.9% ± 8.0, and 5 year overall survival (OS) was 83.3% ± 8.8. Patients older than 9 years at diagnosis (p = 0.002) and those with MC-2 (p = 0.04) had worse 5 year OS. Multi-omic analysis revealed simultaneous activation of multiple signaling pathways, which may serve as potential therapeutic targets. DLGNT remains challenging to treat, with poor outcomes across modalities. Further investigation of treatment, including targeted therapies addressing activated pathways, is needed to improve patient survival.
Keywords: Activated signaling pathways; DLGNT; Diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumor; Patient outcomes; Treatment responses.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G et al (2016) The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta Neuropathol 131:803–820 - PubMed
-
- Bajin IY, Levine A, Dewan MC et al (2024) Understanding diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumors. Childs Nerv Syst 40(8):2359–2366 - PubMed
-
- Deng MY, Sill M, Chiang J et al (2018) Molecularly defined diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumor (DLGNT) comprises two subgroups with distinct clinical and genetic features. Acta Neuropathol 136:239–253 - PubMed
-
- Wiśniewski K, Brandel MG, Gonda DD, Crawford JR, Levy ML (2022) Prognostic factors in diffuse leptomeningeal glioneuronal tumor (DLGNT): a systematic review. Childs Nerv Syst 38(9):1663–1673 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

