Hippocampal Avoidance During Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation for Patients With Small Cell Lung Cancer: Randomized Phase II/III Trial NRG-CC003
- PMID: 40789106
- PMCID: PMC12342643
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO-25-00221
Hippocampal Avoidance During Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation for Patients With Small Cell Lung Cancer: Randomized Phase II/III Trial NRG-CC003
Abstract
Purpose: Hippocampal avoidance (HA) during therapeutic whole-brain radiotherapy reduces the risk of neurocognitive function (NCF) toxicity in patients with brain metastasis. This trial hypothesized that HA during prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) in patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) leads to noninferior intracranial relapse (ICR) and reduction in NCF toxicity.
Methods: This randomized phase II/III trial enrolled patients with SCLC, no brain metastases, and response to chemotherapy. The primary end points were 12-month ICR (noninferiority design, randomized phase II) and 6-month Hopkins Verbal Learning Test-Revised (HVLT-R) Delayed Recall (DR) failure (phase III). Secondary end points were failure in any NCF test, health-related quality of life (HRQOL), overall survival (OS), and toxicity.
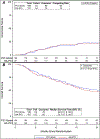
Results: From December 2015 to June 2022, 393 patients were randomly assigned. The median age was 64 years. Stage and memantine usage were balanced. The median follow-up was 17.0 months (all patients) and 30.8 months (alive patients). HA-PCI had noninferior 12-month ICR rate (PCI 14.8% v HA-PCI 14.7%, P < .0001). Six-month HVLT-R DR deterioration was not significantly different (PCI 30.0% v HA-PCI 25.5%, P = .28). Addition of HA to PCI reduced the risk of failure in any NCF test (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.78; 95% CI [0.61 to 0.99]; P = .039). Addition of HA to PCI was not associated with longitudinal change in any HRQOL domain. There were no differences in OS (adjusted HR, 0.88 [95% CI, 0.67 to 1.14]; P = .33) or grade ≥3 toxicity (PCI 31.4% v HA-PCI 30.7%, P = .88).
Conclusion: Although the study did not meet its primary end point of DR preservation, HA during PCI reduces the risk of overall neurocognitive toxicity with noninferior ICR risk and similar survival.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02635009.
Figures
References
-
- Aupérin A, Arriagada R, Pignon JP, et al. : Prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small-cell lung cancer in complete remission. Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation Overview Collaborative Group. N Engl J Med 341:476–84, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Slotman B, Faivre-Finn C, Kramer G, et al. : Prophylactic cranial irradiation in extensive small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 357:664–72, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Takahashi T, Yamanaka T, Seto T, et al. : Prophylactic cranial irradiation versus observation in patients with extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18:663–671, 2017 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous