Temporal optimization of CD25-biased IL-2 agonists and immune checkpoint blockade leads to synergistic anticancer activity despite robust regulatory T cell expansion
- PMID: 40789741
- PMCID: PMC12352230
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010465
Temporal optimization of CD25-biased IL-2 agonists and immune checkpoint blockade leads to synergistic anticancer activity despite robust regulatory T cell expansion
Abstract
Background: Interleukin-2 (IL-2) immunotherapy can induce durable tumor remissions, but its clinical performance has been limited by significant drawbacks such as short serum half-life and high toxicity. Administration of IL-2 in complex with certain anti-IL-2 antibodies (IL-2cx) enhances circulation half-life while also selectivity directing the cytokine to particular immune cell subsets. In particular, IL-2cx has been developed that targets either cells expressing the CD25-containing high-affinity IL-2 receptor (ie, CD25-biased IL-2cx) or cells expressing the CD25-lacking intermediate-affinity IL-2 receptor (ie, CD25-blocking IL-2cx). Since regulatory T (Treg) cells primarily express the high-affinity IL-2 receptor whereas naïve effector T and natural killer cells mainly express the low-affinity IL-2 receptor, CD25-blocking IL-2cx have traditionally been considered as potential cancer therapeutics, particularly in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs).
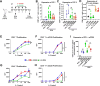
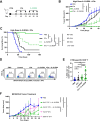
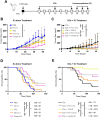
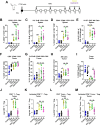
Methods: Stimulation of antigen-primed T cells by IL-2cx in the absence or presence of ICIs was evaluated through adoptive transfer of primed ovalbumin-specific T cells and analysis of expansion. Effects of IL-2cx on Treg cell-mediated inhibition of CD8+ T cells were assessed by flow cytometry and thymidine incorporation. Tumor-bearing mice received combination treatments comprizing IL-2cx and ICIs, where complexes were delivered either before or after ICIs. Tumor growth and mouse survival were monitored, and immune cell phenotyping was performed. Toxicity was determined by tracking body weight, temperature, and lung edema. Substitution of IL-2cx with single-agent cytokine/antibody fusion proteins (immunocytokines, ICs) was also explored.
Results: We showed that CD25-biased IL-2cx and ICs synergize with ICIs to completely eradicate large, established tumors despite robust Treg cell expansion. Importantly, we found that timing is crucial, as administration of IL-2cx after (but not before) ICIs led to profound antitumor effects. Mechanistically, CD25-biased IL-2cx selectively stimulated expansion and effector functions of tumor-specific CD8+ T cells in a CD25-dependent manner, overcoming Treg cell-mediated suppression. Moreover, CD25-biased IL-2cx showed much lower toxicity than CD25-blocking IL-2cx, enabling a larger therapeutic window. Furthermore, we demonstrated that administration of a human IL-2-based IC significantly enhanced the antitumor activity of ICIs, establishing the translational relevance of our work.
Conclusions: Our findings support the temporally optimized use of CD25-biased IL-2-based therapeutics in combination with ICIs for cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: Cytokine; Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor; Immunotherapy; T cell; T regulatory cell - Treg.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JS and MK are listed as co-inventors on a patent entitled “Methods and materials for targeted expansion of immune effector cells”, which bears International Application Number PCT/US2020/039857. DV and JS are listed as co-inventors on a patent entitled “Methods and materials for targeted expansion of regulatory T cells”, which bears International Application Number PCT/US2020/039854. All other authors have no competing interests to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ANV600 is a novel PD-1 targeted IL-2Rβγ agonist that selectively expands tumor antigen-specific T cells and potentiates PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor therapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Jul 15;13(7):e011905. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2025-011905. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40664449 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Oncolytic reovirus enhances the effect of CEA immunotherapy when combined with PD1-PDL1 inhibitor in a colorectal cancer model.Immunotherapy. 2025 Apr;17(6):425-435. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2025.2501926. Epub 2025 May 12. Immunotherapy. 2025. PMID: 40353308
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors plus platinum-based chemotherapy compared to platinum-based chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for first-line treatment of older people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Aug 13;8(8):CD015495. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015495. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39136258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Topalian SL, et al. Treatment of 283 consecutive patients with metastatic melanoma or renal cell cancer using high-dose bolus interleukin 2. JAMA. 1994;271:907–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
