Genetic variation at transcription factor binding sites largely explains phenotypic heritability in maize
- PMID: 40789919
- PMCID: PMC12425805
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-025-02246-7
Genetic variation at transcription factor binding sites largely explains phenotypic heritability in maize
Abstract
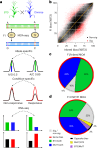
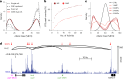
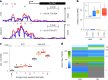
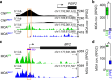
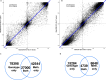
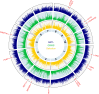
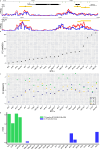
Comprehensive maps of functional variation at transcription factor (TF) binding sites (cis-elements) are crucial for elucidating how genotype shapes phenotype. Here, we report the construction of a pan-cistrome of the maize leaf under well-watered and drought conditions. We quantified haplotype-specific TF footprints across a pan-genome of 25 maize hybrids and mapped over 200,000 variants, genetic, epigenetic, or both (termed binding quantitative trait loci (bQTL)), linked to cis-element occupancy. Three lines of evidence support the functional significance of bQTL: (1) coincidence with causative loci that regulate traits, including vgt1, ZmTRE1 and the MITE transposon near ZmNAC111 under drought; (2) bQTL allelic bias is shared between inbred parents and matches chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing results; and (3) partitioning genetic variation across genomic regions demonstrates that bQTL capture the majority of heritable trait variation across ~72% of 143 phenotypes. Our study provides an auspicious approach to make functional cis-variation accessible at scale for genetic studies and targeted engineering of complex traits.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Chia, J.-M. et al. Maize HapMap2 identifies extant variation from a genome in flux. Nat. Genet.44, 803–807 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Lorant, A., Ross-Ibarra, J. & Tenaillon, M. Genomics of long- and short-term adaptation in maize and teosintes. in Statistical Population Genomics (ed. Dutheil, J. Y.) 289–311 (Springer, 2020). 10.1007/978-1-0716-0199-0_12 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 101081770/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
- 390686111/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 458854361/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- ANR-22-CPJ2-0110-01/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- 1744592/National Science Foundation (NSF)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

