Metformin and berberine synergistically improve NAFLD via the AMPK-SREBP1-FASN signaling pathway
- PMID: 40790070
- PMCID: PMC12339966
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-15495-7
Metformin and berberine synergistically improve NAFLD via the AMPK-SREBP1-FASN signaling pathway
Abstract
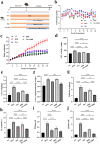
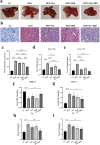
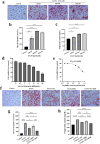
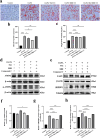
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent metabolic condition linked to dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, and persistent inflammation. Due to its complex pathogenesis, no approved pharmacological treatments currently exist. The research sought to explore the combined impact of metformin (Met) and berberine (BBR) on NAFLD, focusing on the AMPK-SREBP1-FASN pathway implicated in liver lipid regulation. The study design incorporated in both living organisms and laboratory conditions to examine how these interventions influenced NAFLD-associated metabolic abnormalities. The HFD-fed mice provided insight into systemic effects, while the OA/PA-stimulated HepG2 cells offered a controlled environment to investigate cellular mechanisms. By employing this dual approach, the researchers could thoroughly characterize the efficacy of Met, BBR, and their combination in mitigating metabolic disturbances. An Adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase(AMPK) inhibitor was used in cellular experiments to verify the AMPK-dependent mechanism. Our findings highlight that compared to monotherapies, combination treatment significantly enhanced AMPK activation and inhibited sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1) expression and that of its downstream target fatty acid synthase (FASN). In HepG2 cells, these effects were partially reversed by the AMPK inhibitor, confirming AMPK dependence. In vivo, the combined therapy effectively inhibited body weight gain, reduced visceral fat accumulation, improved insulin sensitivity, and attenuated hepatic steatosis and inflammation. The combination of metformin and berberine exerts synergistic effects in ameliorating NAFLD by activating AMPK, downregulating SREBP1 and FASN, and improving lipid metabolism. These findings provide evidence supporting a potentially effective multi-modal treatment approach for NAFLD.
Keywords: AMPK signaling; Berberine; Metformin; NAFLD; Synergistic therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical compliance: This research was conducted in strict accordance with the “National Standards for Laboratory Animal Care and Use” and adhered to the ethical guidelines established by the Animal Experiment Ethics Committee of Shandong First Medical University Affiliated Cancer Hospital. The study received formal ethical approval (Approval No.: SDTHEC2024007033) to ensure all procedures met institutional and regulatory requirements.
Figures


References
-
- Ratziu, V. Starting the battle to control non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Lancet385, 922–924 (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 8227071910/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 8227071910/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 8227071910/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 8227071910/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 8227071910/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 8227071910/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 8227071910/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 8227071910/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- ZR2021MH060/the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- ZR2021MH060/the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- ZR2021MH060/the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- ZR2021MH060/the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- ZR2021MH060/the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- ZR2021MH060/the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- ZR2021MH060/the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- ZR2021MH060/the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province
- KC2023-JX-0288-FZ125/the Beijing Science and Technology Innovation Medical Development Foundation Research Fund Project
- KC2023-JX-0288-FZ125/the Beijing Science and Technology Innovation Medical Development Foundation Research Fund Project
- KC2023-JX-0288-FZ125/the Beijing Science and Technology Innovation Medical Development Foundation Research Fund Project
- KC2023-JX-0288-FZ125/the Beijing Science and Technology Innovation Medical Development Foundation Research Fund Project
- KC2023-JX-0288-FZ125/the Beijing Science and Technology Innovation Medical Development Foundation Research Fund Project
- KC2023-JX-0288-FZ125/the Beijing Science and Technology Innovation Medical Development Foundation Research Fund Project
- KC2023-JX-0288-FZ125/the Beijing Science and Technology Innovation Medical Development Foundation Research Fund Project
- KC2023-JX-0288-FZ125/the Beijing Science and Technology Innovation Medical Development Foundation Research Fund Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

