Immunologic profiling of the infant immune response to whole-cell and acellular pertussis vaccines
- PMID: 40790123
- PMCID: PMC12340008
- DOI: 10.1038/s41541-025-01170-5
Immunologic profiling of the infant immune response to whole-cell and acellular pertussis vaccines
Abstract
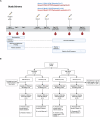
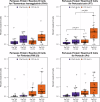
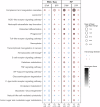
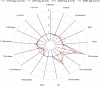
Despite robust antibody responses, immunity induced by acellular pertussis vaccine (DTaP) wanes over time and risk of pertussis seems to be lower in children who receive whole-cell vaccine (DTP) as their first dose. To interrogate the early immunologic response to pertussis vaccine, we enrolled 56 healthy infants who received either DTP or DTaP at 2-, 4-, 6-, and 18-months of age. RNA-sequencing and ribosome profiling of PBMC were performed prior to vaccination (Day 1) and on either Day 2 or Day 8. Pathway enrichment analysis on Days 2 and 8 showed enrichment of TLR-signaling and FcϒR-mediated phagocytosis among DTP recipients. DTP also led to increases in IRAK-4 and IL-1ß. After booster vaccination, a higher frequency of PT-specific B-cells was observed in DTP- vs. DTaP recipients. These data provide insights into the early immunologic responses to pertussis vaccine and may guide next-generation pertussis vaccine development.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors (except C.B.C., J.E.C., C.F.L. and K.M.E.) declare no financial or non-financial competing interests and no conflicts of interest related to the published work. C.B.C. received funding from Moderna, NIH, and CDC and is a consultant to TDCowen, Guidepoint Global, GSK, Sanofi, Merck, and Delbiopharm. He also serves as a member of Data and Safety Monitoring Boards for GSK and Bavarian Nordic and receives royalties from UpToDate. J.E.C. is a former member of the Scientific Advisory Boards of Gigagen (Grifols) and BTG International, has consulted for Moderna, is founder of IDBiologics and receives royalties from UpToDate. The laboratory of J.E.C. received unrelated sponsored research agreements from IDBiologics during the conduct of the study. Vanderbilt University has applied for a patent from unrelated work covering human monoclonal antibodies for pertussis. C.F.L. has funding from and is a consultant to HilleVax. He is also a member of a Data and Safety Monitoring Board of Merck. K.M.E. has funding from NIH and CDC and is a consultant for Bionet, Dynavax and IBM. She is also a member of the Data and Safety Monitoring Boards of Sanofi, X-4 Pharma, Seqirus, Moderna, Pfizer, Merck, Roche, Novavax, and Brighton Collaboration.
Figures
References
-
- Yeung, K. H. T., Duclos, P., Nelson, E. A. S. & Hutubessy, R. C. W. An update of the global burden of pertussis in children younger than 5 years: a modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis.17, 974–980 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Orenstein, W. A. et al. Plotkin’s vaccines, 8th ed. 1782. (Elsevier, 2024).
-
- Klein, N. P. et al. Waning Tdap effectiveness in adolescents. Pediatrics137, e20153326 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Witt, M. A., Katz, P. H. & Witt, D. J. Unexpectedly limited durability of immunity following acellular pertussis vaccination in preadolescents in a North American outbreak. Clin. Infect. Dis.54, 1730–1735 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Decker, M. D. et al. Comparison of 13 acellular pertussis vaccines: adverse reactions. Pediatrics96, 557–566 (1995). - PubMed
Grants and funding
- HSN2722001300023I/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HSN2722001300023I/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HSN2722001300023I/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HSN2722001300023I/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HSN2722001300023I/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HSN2722001300023I/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HSN2722001300023I/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HSN2722001300023I/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HSN2722001300023I/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HSN2722001300023I/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HSN2722001300023I/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HSN2722001300023I/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HSN2722001300023I/NH/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

