A Correlation between Inflammatory Factors and Epileptic Seizures: A Meta-analysis
- PMID: 40791055
- PMCID: PMC12353248
- DOI: 10.62641/aep.v53i4.1790
A Correlation between Inflammatory Factors and Epileptic Seizures: A Meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The pathophysiological mechanisms and relevant biological markers for epileptic seizures largely remained unknown. However, several studies have reported elevated levels of inflammatory factors in the serum of individuals with epileptic seizures. Therefore, this study aims to explore the relationship between inflammatory factors and epileptic seizures.
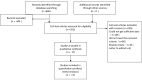
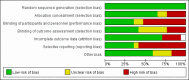
Methods: We retrieved relevant literature published in various databases, including Embase, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, China Wanfang, HowNet, Chinese Biomedical Literature, and VIP, from inception to December 2023. The relationship between inflammatory factors, such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and epileptic seizure was assessed. The selected manuscripts were evaluated based on the predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria, and relevant data were extracted for meta-analysis using Rev Man 5.0 software (RevMan, Oxford, UK) and Stata 12.
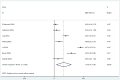
Results: We observed that individuals with epileptic seizures had significantly elevated levels of IL-1β (random-effects model, Standardized Mean Difference (SMD) = 1.87, 95% confidence interval (CI) = [1.17, 2.56], I2 = 96.6%, p = 0.010), IL-6 (SMD = 1.73, 95% CI = [0.41, 3.05], I2 = 96.9%, p = 0.010), and TNF-α (random-effects model, SMD = 2.16, 95% CI = [1.13, 3.18], I2 = 96.5%, p = 0.010). Moreover, the subgroup analysis indicated significant differences between the two groups for the country (origin of publication) (SMD = 1.87, 95% CI = [1.17, 2.56], I2 = 96.6%, p < 0.001), sampling time (SMD = 1.87, 95% CI = [1.17, 2.56], I2 = 96.6%, p = 0.010), and sample source (SMD = 1.87, 95% CI = [1.17, 2.56], I2 = 96.6%, p = 0.010).
Conclusion: The IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels are increased in individuals with epileptic seizures, which could serve as effective biomarkers for epileptogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Weiss A, Canetti L, David SB, Reuveni I, Ekstein D. Seizure phobia: A distinct psychiatric disorder among people with epilepsy. Seizure . 2022;95:26–32. - PubMed
-
- Rajasekar MK, Balasubramanian N. DOAJ (DOAJ: Directory of Open Access Journals); 2021. Hypoparathyroidism the Cause of Seizure, Misdiagnosed as Epilepsy.
-
- Kanner AM, Bicchi MM. Antiseizure Medications for Adults With Epilepsy: A Review. JAMA . 2022;327:1269–1281. - PubMed
-
- Adjei P, Krishnamoorthy ES, Shorvon S, Schachter S. Vol. 0. Cambridge University Press eBooks; 2017. The Clinical Approach to Investigation and Service Organization of Epilepsy Care in Low-and Middle-income Countries; pp. 67–72.
-
- Radhakrishnan A. Bridging the treatment gap in epilepsy-is there an emerging trend in the use of newer antiepileptic drugs? Neurology India . 2016;64:1140–1142. - PubMed

