A national survey-based method for monitoring noncommunicable disease risk factors among adolescents aged 15-17 years across India
- PMID: 40791644
- PMCID: PMC12337017
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2025.103535
A national survey-based method for monitoring noncommunicable disease risk factors among adolescents aged 15-17 years across India
Abstract
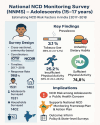
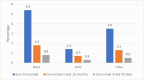
The National Noncommunicable Disease Monitoring Survey (NNMS) was designed to generate nationally representative estimates of key NCD risk factors and contribute to India's national framework for NCD surveillance. This article presents the methodology and key findings related to adolescents aged 15-17 years. The NNMS was a cross-sectional, community-based survey conducted across India during 2017-2018. It was implemented by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the National Centre for Disease Informatics and Research (NCDIR), in collaboration with ten reputed research institutes covering both urban and rural areas. Standardized tools and procedures were employed to ensure consistency and data quality across sites. The survey achieved a high overall response rate of 96.6 %, with participation from 1531 adolescents and 1402 households. Key findings indicate that 3.1 % (95 % CI: 2.0 %-4.7 %) of adolescents reported current daily tobacco use, while 25.2 % (95 % CI: 22.2 %-28.5 %) engaged in insufficient physical activity. Conversely, 74.8 % (95 % CI: 71.5 %-77.8 %) met recommended physical activity levels. Information on dietary behaviors and alcohol use was also collected. As the first nationally representative survey focusing on adolescent NCD risk factors, the NNMS provides crucial baseline data to support India's NCD Action Plan and inform future prevention and control strategies at national and sub-national levels.•This study presents the first nationally representative methodology to estimate NCD risk factors among Indian adolescents aged 15-17 years.•Multistage, community-based sampling design and digital data collection protocol ensured high coverage and data quality across 27 states.•The method is adaptable for state-level surveillance and supports national action plans for adolescent NCD prevention and control.
Keywords: Alcohol consumption; Cross-sectional study; NCD risk factors; Prevalence; Tobacco use.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization Non-Communicable Diseases. 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicablediseases Available from: [Accessed Nov 22, 2024]
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation GBD Compare. 2019. http://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare Available from. [Accessed Dec 08, 2024]
-
- World Health Organization Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of NCDs 2013–2020. 2013. https://www.who.int/publicationsdetail-redirect/9789241506236 Available from: [Accessed December 10, 2024]
-
- World Health Organization National Action Plan and Monitoring Framework for Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) in India. 2012. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/searo/india/health-topic-pdf/nat... Available from: [Accessed Nov 20, 2024]
-
- Indian Council of Medical Research . The India State-Level Disease Burden Initiative. ICMR, PHFI, and IHME; New Delhi: 2017. Public Health Foundation of India, and Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. India: health of the Nation’s States.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

