Effects of Intratympanic Steroid Therapy in Sudden Hearing Loss in Children: The Clinical Case of an Exceptionally Late Hearing Recovery
- PMID: 40791840
- PMCID: PMC12335661
- DOI: 10.22038/ijorl.2025.83020.3794
Effects of Intratympanic Steroid Therapy in Sudden Hearing Loss in Children: The Clinical Case of an Exceptionally Late Hearing Recovery
Abstract
Introduction: Sudden hearing loss represents a medical emergency that can potentially have a highly negative impact on an individual's quality of life. In particular it can represent a serious concern in pediatric age, interfering cognitive and language development. Despite the seriousness of the problem, there is currently no consensus on diagnostic and therapeutic management methods, and the debate is still open.
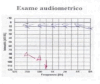
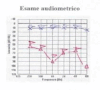
Case report: We present the case of a 15-year-old child with a sudden right-sided hearing loss of profound degree and of idiopathic etiology. Initially he was treated with oral steroid treatment and subsequently to multiple sessions of hyperbaric oxygen therapy without satisfactory results. Several weeks after the onset of symptoms, the patient underwent a cycle of 3 intratympanic methylprednisolone injections with unexpected hearing recovery.
Conclusions: Intratympanic steroid therapy could represent not only a life-saving therapeutic choice as it is currently considered, but also a first therapeutic choice, particularly in pediatric age, thanks to substantial absence of systemic side effects and the potential efficacy even after many weeks from the onset of symptoms.
Keywords: Childhood; Children; Intratympanic steroid therapy; Profound hearing loss; Sudden hearing loss.
©2025 Mashhad University of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
We addressed no conflict of interest, and no funding was required.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
