Diagnostic accuracy of convolutional neural networks in classifying hepatic steatosis from B-mode ultrasound images: a systematic review with meta-analysis and novel validation in a community setting in Telangana, India
- PMID: 40791854
- PMCID: PMC12337209
- DOI: 10.1016/j.lansea.2025.100644
Diagnostic accuracy of convolutional neural networks in classifying hepatic steatosis from B-mode ultrasound images: a systematic review with meta-analysis and novel validation in a community setting in Telangana, India
Abstract
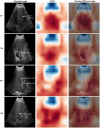
Background: Ultrasound is a widely available, inexpensive, and non-invasive modality for evaluating hepatic steatosis (HS). However, the scarcity of radiological expertise limits its utility. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have potential for automated classification of HS using B-mode ultrasound images. We aimed to assess their diagnostic accuracy and generalisability across diverse study settings and populations.
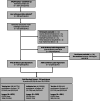
Methods: We systematically reviewed two biomedical databases up to Dec 12, 2023, to identify studies that applied CNNs in the classification of HS using B-mode ultrasound images as input (PROSPERO: CRD42024501483). We supplemented this review with a novel analysis of the community-based Andhra Pradesh Children and Parents' Study (APCAPS) in India to address the overrepresentation of hospital samples and lack of data on South Asian populations who exhibit a distinct central adiposity phenotype that could influence CNN performance. We quantitatively synthesised diagnostic accuracy metrics for eligible studies using random-effects meta-analyses.
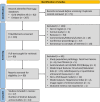
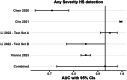
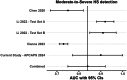
Findings: Our search returned 289 studies, of which 17 were eligible. All but one of the 17 studies were based in hospital or clinical outpatient settings with curated cases and controls. Studies were conducted exclusively in East Asian, European, or North American populations. Studies employed varying gold standards: seven studies (41.18%) used liver biopsy, three (17.64%) used MRI proton density fat fraction, and seven (41.18%) used clinician-evaluated ultrasound-based HS grades. The APCAPS sample included 219 participants with radiologist-assigned HS grades. Across the range of study settings and populations, CNNs demonstrated good diagnostic accuracy. Meta-analysis of studies with low risk of bias reporting on five unique datasets showed a pooled area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.93 (95% CI 0.73-0.98) for detecting any severity and 0.86 (95% CI 0.77-0.92) for detecting moderate-to-severe HS severity grades, respectively.
Interpretation: CNNs have good diagnostic accuracy and generalisability for HS classification, suggesting potential for real-world application.
Funding: Medical Research Council, UK (MR/T038292/1, MR/V001221/1).
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Convolutional neural networks; Fatty liver disease; Machine learning; Ultrasonography.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
AJ and PM received research funding (salary support) from Medical Research Council, UK. We declare no other competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence for diagnosing exudative age-related macular degeneration.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Oct 17;10(10):CD015522. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015522.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39417312
-
Development and Validation of a Convolutional Neural Network Model to Predict a Pathologic Fracture in the Proximal Femur Using Abdomen and Pelvis CT Images of Patients With Advanced Cancer.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023 Nov 1;481(11):2247-2256. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002771. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023. PMID: 37615504 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Magnetic resonance perfusion for differentiating low-grade from high-grade gliomas at first presentation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 22;1(1):CD011551. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011551.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29357120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Virarkar M., Szklaruk J., Jensen C.T., Taggart M.W., Bhosale P. What's new in hepatic steatosis. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2021;42:405–415. - PubMed
-
- Riazi K., Azhari H., Charette J.H., et al. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7:851–861. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

