Exploring whey and faba bean protein interactions at the oil-water interface: A combined drop tensiometry and microfluidicsstudy
- PMID: 40792111
- PMCID: PMC12337646
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2025.101158
Exploring whey and faba bean protein interactions at the oil-water interface: A combined drop tensiometry and microfluidicsstudy
Abstract
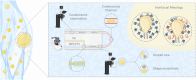
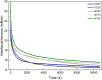
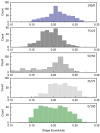
The interfacial properties of model oil-water interfaces stabilized by faba bean protein isolate (FPI), whey protein isolate (WPI), and their mixtures were investigated. Two complementary techniques, microfluidics-based analysis and drop tensiometry were employed to study the impact of protein mixing on interfacial tension, adsorption kinetics, and droplet stability. A microfluidic platform was used for droplet generation and single droplet analysis, assessing the impact of protein blending on droplet size and shape eccentricity after droplet generation. Drop tensiometry complemented the microfluidics-based analysis by evaluating interfacial tension and viscoelastic properties of the various interfaces. The presence of FPI altered WPI interfaces; in mixed systems, antagonistic interactions between proteins resulted in a decreased elastic modulus and broadening of the shape eccentricity. Mixed systems resulted in smaller droplets with narrower size distributions and increased resistance to short-term coalescence with respect to emulsion droplets stabilized by FPI alone, and droplet stability increased proportionally with WPI/FPI ratio.
Keywords: Emulsifying properties; Faba bean proteins; Microfluidics; Oil/water interface; Protein adsorption; Protein mixing; Whey proteins.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Behavior of plant-dairy protein blends at air-water and oil-water interfaces.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020 Aug;192:111015. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111015. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020. PMID: 32416469
-
Fermented insoluble fiber enhances the emulsifying property and bioaccessibility of essential oil emulsion with its whey protein isolate conjugates and chitosan.J Sci Food Agric. 2025 Aug 30;105(11):5906-5921. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.14299. Epub 2025 Apr 28. J Sci Food Agric. 2025. PMID: 40290072
-
Inter cross-linking microgels by superchaotropic nano-ions at interface: Controlled stabilization of emulsions.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2025 Dec;699(Pt 2):138257. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2025.138257. Epub 2025 Jun 21. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2025. PMID: 40609163
-
Tamponade in surgery for retinal detachment associated with proliferative vitreoretinopathy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Feb 14;2(2):CD006126. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006126.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 13;5:CD006126. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006126.pub4. PMID: 24532038 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Portion, package or tableware size for changing selection and consumption of food, alcohol and tobacco.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 14;2015(9):CD011045. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011045.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26368271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Badjona, A., Bradshaw, R., Millman, C., Howarth, M., & Dubey, B. Faba beans protein as an unconventional protein source for the food industry: processing influence on nutritional, techno-functionality, and bioactivity. Food Rev. Int., 1-25. https://doi.org/ 10.1080/87559129.2023.2245036. - DOI
-
- Bandyopadhyay M., Nickerson M.T., Ghosh S. Effect of mild fractionation conditions on the composition, interfacial and emulsifying properties of water-soluble fractions from faba bean flour. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025 doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2025.101763. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

