miR-490-5p inhibits the progression of osteosarcoma by targeting HDAC2
- PMID: 40792134
- PMCID: PMC12335688
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-2024-2217
miR-490-5p inhibits the progression of osteosarcoma by targeting HDAC2
Abstract
Background: Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most prevalent malignant bone tumor and has a particularly unfavorable prognosis. Although miR-490-5p is regarded as an established diagnostic and predictive marker for human cancers, the role of miR-490-5p in OS remains presently unclear. The aim of this study was to clarify the function of miR-490-5p in OS.
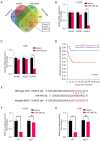
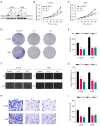
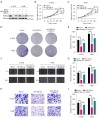
Methods: Bioinformatics analysis of OS cells was performed to identify differentially expressed microRNAs (miRNAs, miRs). Then, the expression profiles of miR-490-5p in various OS cells were determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis. The roles of miR-490-5p in OS cells were assessed through in vitro cytological experiments. Bioinformatics methods were used to predict target genes. The relationship between miR-490-5p and HDAC2 was demonstrated by a dual-luciferase reporter gene assay.
Results: Expression of miR-490-5p was relatively decreased in OS cells. Overexpression of miR-490-5p inhibited proliferation and metastasis of OS cells. Moreover, miR-490-5p was found to negatively regulate HDAC2 as a downstream target gene. Recovery experiments confirmed that HDAC2 overexpression rescued the inhibitory effect on OS progression by overexpression of miR-490-5p.
Conclusions: MiR-490-5p directly regulated HDAC2 expression, thereby modulating the growth and metastatic capacity of OS cells. The miR-490-5p/HDAC2 axis could serve as a promising therapeutic target for OS.
Keywords: HDAC2; Osteosarcoma (OS); metastasis; miR-490-5p; proliferation.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-2024-2217/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B virus core/capsid protein induces hepatocellular carcinoma progression via long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1/miR-335-5p/CDC7 axis.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Jun 30;14(6):3319-3335. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2025-233. Epub 2025 Jun 16. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40687256 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-150-5p inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting FTO in osteosarcoma.Oncol Res. 2024 Oct 16;32(11):1777-1789. doi: 10.32604/or.2024.047704. eCollection 2024. Oncol Res. 2024. PMID: 39449798 Free PMC article.
-
New mechanism of miR-34a-5p in regulating the biological behavior of osteosarcoma by targeting FoxM1.Cytotechnology. 2025 Jun;77(3):90. doi: 10.1007/s10616-025-00758-y. Epub 2025 Apr 21. Cytotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40271388
-
Long noncoding RNA TUG1 promotes malignant progression of osteosarcoma by enhancing ZBTB7C expression.Biomed J. 2024 Jun;47(3):100651. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2023.100651. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Biomed J. 2024. PMID: 37562773 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in oral fluids (saliva and gingival crevicular fluid) as biomarkers in orthodontics: systematic review and integrated bioinformatic analysis.Prog Orthod. 2021 Oct 11;22(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s40510-021-00377-1. Prog Orthod. 2021. PMID: 34632546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sayles LC, Breese MR, Koehne AL, et al. Genome-Informed Targeted Therapy for Osteosarcoma. Cancer Discov 2019;9:46-63. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-1152 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
