Morphological and Phylogenetic Characterization of Endophytic Fungi Isolated from Brown Algae (Phaeophyceae) in Korea
- PMID: 40792186
- PMCID: PMC12337722
- DOI: 10.1080/12298093.2025.2535776
Morphological and Phylogenetic Characterization of Endophytic Fungi Isolated from Brown Algae (Phaeophyceae) in Korea
Abstract
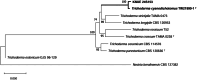
Seaweed-associated endophytic fungi have recently attracted considerable attention due to their ecological significance and potential application as biological resources. Accordingly, research efforts to isolate and characterize fungal endophytes from marine macroalgae have accelerated. This study aimed to isolate and identify endophytic fungi from two brown algae, Sargassum thunbergii and S. muticum, collected from intertidal zones in Tongyeong and Pohang, Korea. Identification was performed based on morphological characteristics and multilocus phylogenetic analyses using ITS, LSU, TEF1, TUB2, and RPB2 gene sequences. As a result, three previously unrecorded fungal species in Korea were identified: Neopyrenochaeta telephoni, Trichoderma cyanodichotomum, and Microascus intricatus. This study provides detailed descriptions of their morphological features and phylogenetic relationships. These findings contribute to a better understanding of fungal diversity associated with brown algae in Korea and highlight the potential significance of endophytic fungi in marine ecosystems.
Keywords: Brown algae; Phylogenetic analysis; endophytic fungi; sargassum; seaweed-associated fungi.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group on behalf of the Korean Society of Mycology.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures





References
-
- Redmond S, Kim JK, Yarish C, et al. Culture of Sargassum in Korea: techniques and potential for culture in the US. Orono, ME: Maine Sea Grant College Program; 2014.
-
- Singh VK, Dwivedy AK, Singh A, et al. Fungal endophytes from seaweeds: an overview. In: Patra JK, Das G, Shin HS, editors. Microbial biotechnology: volume 2. Application in food and pharmacology. Singarpore: Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd; 2018. p. 483–498.
-
- Ji N-Y, Wang B-G.. Mycochemistry of marine algicolous fungi. Fungal Divers. 2016;80(1):301–342. doi: 10.1007/s13225-016-0358-9. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
