Antibacterial efficacy of sodium dichloroisocyanurate and 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid intracanal medicaments on Enterococcus faecalis: A comparative in-vitro study
- PMID: 40792197
- PMCID: PMC12335985
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2025.07.015
Antibacterial efficacy of sodium dichloroisocyanurate and 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid intracanal medicaments on Enterococcus faecalis: A comparative in-vitro study
Abstract
Background: Optimal healing of periapical tissues by completely eradicating root canal infection is the primary goal of endodontic therapy. The use of intracanal medication enhances the antibacterial efficacy of endodontic treatment.
Aim: Comparative evaluation of antibacterial efficacy of intracanal medicaments such as sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC) and 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid (HICA) with a formulation of calcium hydroxide (Ca (OH)2) and 2 % chlorhexidine gluconate (CHX) against Enterococcus faecalis(E.faecalis).
Methodology: Fifty-two single-rooted teeth were subjected to endodontic instrumentation and inoculation with E. faecalis microbial suspension. After 14 days, the root canals of each tooth were ground with a Peeso reamer to procure the dentine chips. Colony-forming units (CFU-1) were counted after 24 h of incubation. Intracanal medicaments: NaDCC, HICA, and (Ca (OH)2) plus 2 % CHX were placed in the tooth and incubated for 14 days. The antibacterial effects of the intracanal medicaments were measured using CFU testing at three-time intervals.
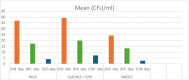
Results: Inter-group analysis utilized one-way ANOVA for statistical analysis, and within-group analysis employed repeated-measures ANOVA followed by the Tukey post hoc test. NaDCC exhibited a significantly lower CFU count compared to HICA (p-value = .000) and Ca (OH)2 + 2 % CHX (p-value = .000). HICA showed a significantly lower CFU count than Ca (OH)2 + 2 % CHX (p-value = .009) after 24 h.
Conclusion: NaDCC and HICA demonstrate potent antimicrobial efficacy against E. faecalis, suggesting their potential as an alternative intracanal medicament for endodontic infection.
Keywords: 2-Hydroxyisocaproic acid; Antimicrobial effect; Calcium hydroxide; Chlorhexidine; Intracanal medicament; Sodium dichloroisocyanurate.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None. The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sakko M., Tjäderhane L., Sorsa T., Hietala P., Rautemaa R. 2-Hydroxyisocaproic acid is bactericidal in human dental root canals ex vivo. Int Endod J. 2017 May;50(5):455–463. - PubMed
-
- Siqueira J.F., Rôças I.N. Clinical implications and microbiology of bacterial persistence after treatment procedures. J Endod. 2008 Nov;34(11):1291–1301.e3. - PubMed
-
- Siqueira J.F., Magalhães K.M., Rôças I.N. Bacterial reduction in infected root canals treated with 2.5% NaOCl as an irrigant and calcium hydroxide/camphorated paramonochlorophenol paste as an intracanal dressing. J Endod. 2007 Jun;33(6):667–672. - PubMed
-
- Tronstad L., Andreasen J.O., Hasselgren G., Kristerson L., Riis I. pH changes in dental tissues after root canal filling with calcium hydroxide. J Endod. 1981 Jan;7(1):17–21. - PubMed
-
- de Almeida Gomes B.P.F., Vianna M.E., Sena N.T., Zaia A.A., Ferraz C.C.R., de Souza Filho F.J. In vitro evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of calcium hydroxide combined with chlorhexidine gel used as intracanal medicament. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006 Oct;102(4):544–550. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

