Colopathy associated with pentosan polysulfate use
- PMID: 40792210
- PMCID: PMC12336275
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1494467
Colopathy associated with pentosan polysulfate use
Abstract
Introduction: We describe a novel colopathy associated with pentosan polysulfate (PPS) use and assess the strength of the drug-disease association in a two-part investigation.
Methods: 1. Cohort Study: We studied individuals with a history of long-term PPS use. Case histories concerning gastrointestinal disease were obtained with review of endoscopy records and histopathology specimens. Findings were summarized with descriptive statistics. 2. Cross-Sectional Study: We evaluated patients with interstitial cystitis at a single clinical center. We obtained data on drug exposure and medical histories and measured the strength of association between PPS use and diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) using multivariate logistic regression.
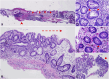
Results: 1. Cohort Study: Among 13 participants, the median PPS exposure was 2.04 kg (range 0.99-2.54 kg). Eleven participants (84.6%) developed IBD symptomatology after initiating PPS therapy, and 9 (69.2%) were diagnosed with IBD. Two others (18%) were diagnosed with irritable bowel syndrome. Of the 10 participants with endoscopic and histopathologic data, six had abnormal colonic mucosa on endoscopy, and all 10 had histologic abnormalities. Clinical and histologic improvement was noted after PPS cessation, though two (18%) required colectomy for colitis-associated dysplasia. 2. Cross-Sectional Study: Among 219 subjects with interstitial cystitis, PPS use was a statistically significant predictor of an IBD diagnosis, with an adjusted odds ratio of 3.3 (95% confidence interval, 1.2-8.8, p = 0.02).
Discussion: Our study identifies a strong association between PPS use and clinical diagnosis of IBD. Histopathologic findings suggest a novel drug-associated colopathy, with some subjects necessitating colectomy for dysplasia. Further investigation into the causality of this association is warranted.
Keywords: colopathy; dextran sodium sulfate; elmiron; inflammatory bowel disease; interstitial cystitis; irritable bowel syndrome; pentosan polysulfate; toxicity.
Copyright © 2025 Jung, Zheng, Weiss, Mathew, Meyer, Nizam, Iskandar and Jain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Update of
-
Colopathy Associated with Pentosan Polysulfate Use.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 4:2023.04.03.23288071. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.03.23288071. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 28;16:1494467. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1494467. PMID: 37066211 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Arlov Ø., Rütsche D., Korayem M. A., Öztürk E., Zenobi‐Wong M. (2021). Engineered sulfated polysaccharides for biomedical applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31 (19). 10.1002/adfm.202010732 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

