Efficacy and safety of D-TACE followed by D-RFA for unresectable large hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 40792272
- PMCID: PMC12336487
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1530951
Efficacy and safety of D-TACE followed by D-RFA for unresectable large hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the safety and short-term clinical efficacy of drug-loaded polyvinyl alcohol microspheres transarterial chemoembolization (D-TACE) in the treatment of unresectable large liver carcinoma with sequential double-needle water-cooled circulating radiofrequency ablation (D-RFA).
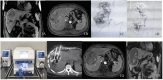
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed for patients with large hepatocellular carcinoma who underwent sequential D-TACE with D-RFA treatment at our hospital. From May 2019 to May 2023, a total of 143 intrahepatic malignant lesions were treated, and a total of 110 D-TACE and 96 D-RFA interventional therapy procedures were performed. The short-term efficacy at 1, 3, and 6 months after interventional therapy was analyzed based on the modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumor (2020 edition) criteria. The evaluation included the efficacy of local tumor control, feasibility of technical implementation, safety of surgery, and tolerability by surgical patients.
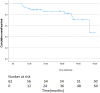
Results: Sixty-two patients underwent successful interventional therapy, achieving good technical feasibility. The objective response rate (ORR) at 3, 6, and 12 months was 90.4%, 85.5%, and 74.2%, respectively. The median overall survival (OS) was 35.0 months (95% CI: 24.7-45.3). The survival rates at 3, 6, and 12 months were 100% (62/62), 96.7% (60/62), and 93.5% (58/62), respectively. No cases of death occurred due to serious complications such as ectopic embolism, tumor rupture, or liver failure within 1 month after surgery. Two cases of postoperative tumor lysis syndrome, 3 cases of pleural effusion caused by intercostal artery injury, and 4 cases of small effusion in the abdominal cavity were reported. Eight cases of mild, moderate, and severe abdominal pain during or after the operation; 6 cases had mild to moderate liver function impairment. Eight patients experienced fever within 1 week after surgery.
Conclusion: The D-TACE with sequential D-RFA technique for the treatment of unresectable large liver cancer is safe and controllable, with a high ORR. This combination treatment provides a useful reference value for the exploration of new treatment modes for advanced liver cancer, but the long-term efficacy evaluation requires multi-center, large-sample clinical studies, and continuous follow-up data analysis.
Keywords: double-needle radiofrequency ablation; drug-loaded microsphere transarterial chemoembolization; hepatocellular carcinoma; large; unresectable.
Copyright © 2025 Pang, Luo, Chen, Zhou, Zhang, Li, Zhao, Yuan and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sintilimab plus lenvatinib in combination with transarterial chemoembolization and subsequent radiofrequency ablation for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-arm, single-center study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 25;15(1):27123. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12858-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40715509 Free PMC article.
-
Transarterial (chemo)embolisation versus systemic chemotherapy for colorectal cancer liver metastases.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Aug 9;8(8):CD012757. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012757.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39119869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of people with early- or very early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: an attempted network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 28;3(3):CD011650. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011650.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28351116 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of transcatheter arterial embolization combined with ablation and regorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma patients failing first-line treatment: a real-world study.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 Jun 30;16(3):1050-1059. doi: 10.21037/jgo-2025-337. Epub 2025 Jun 27. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40672100 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization and PD-1 inhibitor for treatment of unresectable head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: an initial, short-term clinical experience in a single-center retrospective cohort study.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 23;16:1615440. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1615440. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40771818 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

