Enhancing emotional intelligence in medical education: a systematic review of interventions
- PMID: 40792296
- PMCID: PMC12336118
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1587090
Enhancing emotional intelligence in medical education: a systematic review of interventions
Abstract
Introduction: Emotional intelligence (EI) is a crucial competency for medical professionals, facilitating effective interpersonal relationships between physicians and patients. The ability to evaluate, regulate, and apply emotional understanding plays a significant role in fostering empathy, communication, and stress management. This systematic review aimed to determine the impact of various interventions on medical students' EI development, academic performance, and overall patient care.
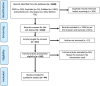
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted for studies published from 2021 until 2024, inclusion criteria focused on studies on medical students, employed validated EI assessment tools, and utilized appropriate research designs.
Results: 44 articles met the inclusion criteria. The Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) Critical Appraisal Checklist was applied to assess the quality of included studies. Although a meta-analysis was initially planned, substantial heterogeneity across the studies limited the pooling of quantitative data. Using an inductive coding approach, eight major themes were identified: Narrative and Storytelling Interventions, Reflective Practices and Writing, Communication Skills Training, Emotional Intelligence Enhancement, Experiential Learning and Patient Exposure, Stress, Burnout, and Coping Interventions, Assessment Tools and Structural Interventions, and Personalized Interventions and Diversity Considerations. These themes were subsequently mapped onto Daniel Goleman's model of Emotional Intelligence to provide a structured theoretical framework.
Discussion: The findings of this review highlight that various interventions hold promise in enhancing EI among medical students, leading to improvements in personal well-being, communication skills, and professional development. The most effective approach appears to be a multifaceted, longitudinal integration of EI-focused strategies throughout medical training, incorporating repeated practice, guided reflection, faculty mentorship, and structured debriefing. The broader implications extend to improved doctor-patient relationships, reduced burnout, and enhanced clinical decision-making, ultimately contributing to higher patient satisfaction and more compassionate healthcare delivery. Future research should focus on refining intervention methodologies and assessing their long-term impact on medical education and practice.
Keywords: emotional intelligence; empathy; medical education; medical students; relationship management; self-awareness; self-management; social awareness.
Copyright © 2025 Maity, De Filippis, Aldanese, McCulloch, Sandor, Perez Cajigas, Antoniadis, Rochester, Carter, Preisig, Kobeissi, Nayak, Mendoza and Nauhria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314
-
Faculty development initiatives designed to promote leadership in medical education. A BEME systematic review: BEME Guide No. 19.Med Teach. 2012;34(6):483-503. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2012.680937. Med Teach. 2012. PMID: 22578043
-
The effectiveness of interventions to meet family needs of critically ill patients in an adult intensive care unit: a systematic review update.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Mar;14(3):181-234. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-2477. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532144
-
The effectiveness of using non-traditional teaching methods to prepare student health care professionals for the delivery of mental state examination: a systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Aug 14;13(7):177-212. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2263. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26455855
-
Effectiveness and experience of arts-based pedagogy among undergraduate nursing students: a mixed methods systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Nov;14(11):139-239. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-003188. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27941518
References
-
- Salovey P, Mayer JD. Emotional intelligence. Imagination Cogn Pers. (1990) 9:185–211. doi: 10.2190/DUGG-P24E-52WK-6CDG - DOI
-
- Hojat M, DeSantis J, Shannon SC, Mortensen LH, Speicher MR, Bragan L, et al. The Jefferson scale of empathy: a nationwide study of measurement properties, underlying components, latent variable structure, and national norms in medical students. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. (2018) 23:899–920. doi: 10.1007/s10459-018-9839-9, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous