Pulse Oximetry Desaturation in the Postoperative Recovery Room in Patients with Obesity and Diabetes Using GLP-1 Agonists: A Retrospective Observational Study
- PMID: 40792324
- PMCID: PMC12338001
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.87774
Pulse Oximetry Desaturation in the Postoperative Recovery Room in Patients with Obesity and Diabetes Using GLP-1 Agonists: A Retrospective Observational Study
Abstract
Background and objectives: Glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists (GLP-1), obesity, and diabetes may delay gastric emptying in some settings. We tested three hypotheses. First, the duration of GLP1-hold is associated with a larger difference between pulse oximetry at room air immediately preoperatively and one hour postoperatively, just prior to discharge home (DSpO2), as a marker of clinically important atelectasis and/or micro-aspiration. Second, we tested the hypothesis that the duration of GLP1-hold affects fasting glucose. Third, we tested the hypothesis that DSpO2 is linked to morbid obesity.
Materials and methods: In this retrospective observational cohort study, we screened the cohort of all 1571 patients undergoing urologic ambulatory surgery in one stand-alone center between September 2023 and September 2024. The inclusion criteria were diabetics using GLP-1 within 30 days, creatinine below 2 mg/dL, and age between 18 and 80 years. The outcomes of fasting glucose and DSpO2 were compared between the groups holding GLP-1 longer and shorter than seven days. The outcome DSpO2 was also compared between the groups with and without morbid obesity, defined generally as a body mass index (BMI) of over 35 kg/m² in the presence of one major comorbidity. All of our study subjects had diabetes mellitus, a major comorbidity.
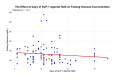
Results: Among all 107 subjects, 56% had laryngeal mask airways and 9% endotracheal tubes. GLP-1 was held 12 ± 8 days (mean ± SD). DSpO2 was 1.5% ± 1.9 with short GLP-1-hold versus 1.8% ± 2.0 with long GLP-1-hold (p=0.41). The mean glucose was 130 mg/dL ± 49 with short GLP1-hold versus 138 mg/dL ± 39 with long GLP-1-hold (p=0.69). DSpO2 was 2.29% ± 1.78 with morbid obesity (N=38) versus 1.43% ± 1.99 without (N=69, p=0.0254, unpaired two-tailed t-test). Patients with morbid obesity showed a trend toward twice the incidence (at 24%) for DSpO2 > 4% (chi-square, p=0.14).
Conclusions: It may be prudent to protect the airway with endotracheal intubation for patients with morbid obesity and diabetes using GLP-1, especially in the lithotomy position.
Keywords: ambulatory surgery; desaturation; diabetes mellitus; gastroparesis; glucagon-like peptide-1; laryngeal mask airway; morbid obesity; subclinical aspiration pneumonia.
Copyright © 2025, Skidmore et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Louisiana State University, Shreveport issued approval (STUDY00002715). Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The quantity, quality and findings of network meta-analyses evaluating the effectiveness of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss: a scoping review.Health Technol Assess. 2025 Jun 25:1-73. doi: 10.3310/SKHT8119. Online ahead of print. Health Technol Assess. 2025. PMID: 40580049 Free PMC article.
-
Preexisting Diabetes and Pregnancy: An Endocrine Society and European Society of Endocrinology Joint Clinical Practice Guideline.Eur J Endocrinol. 2025 Jun 30;193(1):G1-G48. doi: 10.1093/ejendo/lvaf116. Eur J Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40652450
-
Dipeptidyl-peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 analogues for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in people at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 10;5(5):CD012204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012204.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28489279 Free PMC article.
-
Indirect comparative efficacy and safety of tirzepatide 10 and 15 mg versus semaglutide 2.4 mg for the management of obesity and overweight in patients with type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 Sep;27(9):4709-4719. doi: 10.1111/dom.16508. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 40537987 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Relationship between perioperative semaglutide use and residual gastric content: a retrospective analysis of patients undergoing elective upper endoscopy. Silveira SQ, da Silva LM, de Campos Vieira Abib A, et al. J Clin Anesth. 2023;87:111091. - PubMed
-
- Food residue during esophagogastroduodenoscopy is commonly encountered an is not pathognomonic of delayed gastric emptying. Bi D, Choi C, League J, Camilleri M, Prichard DO. Dig Dis Sci. 2021;66:3951–3959. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
