Revisiting the Effect of Udenafil on Exercise Performance in Patients With Fontan Circulation: Results of a Post Hoc Analysis of the FUEL Trial
- PMID: 40792599
- PMCID: PMC12533643
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.125.041348
Revisiting the Effect of Udenafil on Exercise Performance in Patients With Fontan Circulation: Results of a Post Hoc Analysis of the FUEL Trial
Abstract
Background: In the FUEL (Fontan Udenafil Exercise Longitudinal) trial, a positive treatment effect was identified for outcomes at the ventilatory anaerobic threshold but not for the primary outcome, oxygen consumption (Vo2) at peak exercise. This disparate response may be explained by the physiologic challenge of improving peak Vo2 in participants with near-normal baseline exercise performance.
Methods: Participants were divided into subgroups by baseline predicted peak Vo2 (<80% versus ≥80%). Treatment effect was evaluated in those with a baseline peak Vo2 <80% predicted and linear regression was performed to examine the interaction between subgroup and response to therapy for the primary and secondary outcomes.
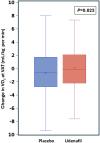
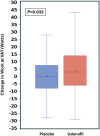
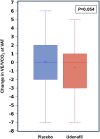
Results: Of the 379 participants with paired exercise data, 302 (80%) had a baseline peak Vo2 <80% predicted. In this subgroup, the primary outcome of peak Vo2 improved significantly after 6 months of udenafil treatment, when compared with placebo (0.23±4.17 mL/kg per min versus -0.90±3.74 mL/kg per min; P=0.021). Secondary outcome measures, including Vo2 at ventilatory anaerobic threshold (P=0.023), work at ventilatory anaerobic threshold (P=0.032), and the myocardial performance index (P=0.007) were all significantly improved as well. A significant interaction was found between exercise subgroups and response to udenafil for peak Vo2 (P=0.036) but not for other outcomes.
Conclusions: In this post hoc subgroup analysis, after exclusion of patients with Fontan circulation with near-normal baseline peak Vo2, a positive treatment effect of udenafil was identified for the primary outcome of peak Vo2. The interaction between baseline peak Vo2 and treatment may have influenced the outcome of the FUEL trial.
Registration: URL: https://clinicaltrials.gov; Unique identifier: NCT0274115.
Keywords: Fontan; exercise; udenafil.
Conflict of interest statement
D.G. has consulted for and received grant funding from Mezzion Pharma Co. Ltd., and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and is a coinventor on a method of use for udenafil in adolescents who have undergone the Fontan procedure. D.P. received a consulting fee from Mezzion Pharma Co. Ltd. J.W. receives funding from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. B.M. is a consultant for Janssen, Chiesi, Esperion, Ultragenyx, and Amryt Pharma. K.H. receives funding from the National Centers for Advancing Translational Sciences. J.Y. was an employee of Mezzion Pharma Co. Ltd. S.P. received grant funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. B.G. is a consultant for Mezzion Pharma Co. Ltd., Medtronic, W. L. Gore, and PECA Labs. The remaining authors have no disclosures to report.
Figures

References
-
- Downing TE, Allen KY, Glatz AC, Rogers LS, Ravishankar C, Rychik J, Faerber JA, Fuller S, Montenegro LM, Steven JM, et al. Long‐term survival after the Fontan operation: twenty years of experience at a single center. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154:243–253 e242. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2017.01.056 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

