Regulation of viral hepatitis by N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation
- PMID: 40793828
- PMCID: PMC12360054
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2025.2544726
Regulation of viral hepatitis by N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation
Abstract
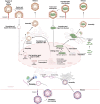
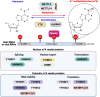
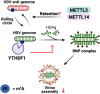
Recent studies have shown that the presence of an RNA modification, N6-methyladenosine (m6A), in viral RNAs during infection significantly impacts the outcome of viral replication and pathogenesis. In particular, various functions of m6A have been elucidated in hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), and hepatitis delta virus (HDV). During viral infection, m6A methylation not only directly affects the replication of these viruses but also regulates diverse cellular RNAs to control pathogenesis. This review aims to explore the functions of m6A modification in the infectious processes and pathogenesis of HBV, HCV, and HDV. Understanding the role of m6A methylation in these viral life cycles is essential for elucidating their pathogenesis and developing novel therapeutic strategies for HBV, HCV, and HDV infections.
Keywords: Hepatitis B virus; N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation; hepatitis C virus; hepatitis Delta virus; viral hepatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
