An Hfq-dependent post-transcriptional mechanism fine tunes RecB expression in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 40794102
- PMCID: PMC12342828
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.94918
An Hfq-dependent post-transcriptional mechanism fine tunes RecB expression in Escherichia coli
Abstract
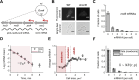
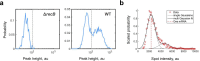
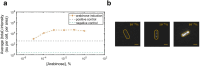
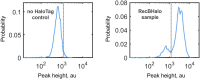
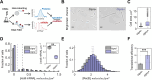
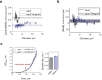
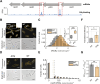
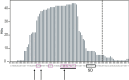
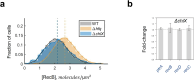
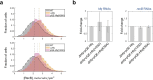
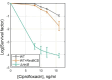
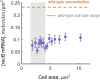
All living organisms have developed strategies to respond to chromosomal damage and preserve genome integrity. One such response is the repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), one of the most toxic forms of DNA lesions. In Escherichia coli, DSBs are repaired via RecBCD-dependent homologous recombination. RecBCD is essential for accurate chromosome maintenance, but its over-expression can lead to reduced DNA repair ability. This apparent paradox suggests that RecBCD copy numbers may need to be tightly controlled within an optimal range. Using single-molecule fluorescence microscopy, we have established that RecB is present in very low abundance at mRNA and protein levels. RecB transcription shows high fluctuations, yet cell-to-cell protein variability remains remarkably low. Here, we show that the post-transcriptional regulator Hfq binds to recB mRNA and downregulates RecB protein translation in vivo. Furthermore, specific disruption of the Hfq-binding site leads to more efficient translation of recB mRNAs. In addition, we observe a less effective reduction of RecB protein fluctuations in the absence of Hfq. This fine-tuning Hfq-mediated mechanism might have the underlying physiological function of maintaining RecB protein levels within an optimal range.
Keywords: DNA repair; E. coli; Hfq protein; RecBCD enzyme; chromosomes; gene expression; noise suppression; physics of living systems; post-transcriptional regulation.
© 2024, Kalita et al.
Conflict of interest statement
IK, II, LM, LG, SG, ME No competing interests declared
Figures


Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2021.10.23.465540
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.94918.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.94918.2
References
-
- Abdennur N. Gillespie. d772e07Github. 2012 https://github.com/nvictus/Gillespie
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

