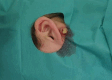
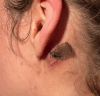
Friend or foe? Sebaceous cyst inflammation during ixekizumab therapy in psoriatic arthritis: case based review
- PMID: 40794191
- PMCID: PMC12343708
- DOI: 10.1007/s00296-025-05949-6
Friend or foe? Sebaceous cyst inflammation during ixekizumab therapy in psoriatic arthritis: case based review
Abstract
Ixekizumab is a monoclonal antibody used in the treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis by targeting interleukin-17 A (IL-17 A). It has demonstrated efficacy in controlling inflammation in autoimmune diseases, though adverse reactions can arise. This case study reports a case of 25-year-old female with psoriatic arthritis undergoing treatment with ixekizumab, who developed acute enlargement and inflammation of a pre-existing sebaceous cyst located posterior to the left auricle, occurring two days after the administration of a routine ixekizumab dose. The present study investigates the potential association between the inflammatory process observed within the cyst and the immunomodulatory mechanisms of ixekizumab. Literature review revealed no prior reports directly linking ixekizumab with sebaceous cyst inflammation. However, related adverse effects, including paradoxical inflammation, infectious complications, and immune dysregulation have been described in patients treated with IL-17 A inhibitors. These include IBD exacerbation, eczematous eruptions, paradoxical psoriasis, and rare systemic complications, suggesting broader immunological effects of IL-17 blockade.
Keywords: Adverse skin reaction; Cutaneous infection; IL-17A inhibitor; Ixekizumab; Psoriatic arthritis; Sebaceous cyst.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: Marta Całus, Julia Grymuza, Anna Baran, Piotr Myśliwiec, and Iwona Flisiak declare that they have no conflict of interest. Ethical approval: As this is a case-based review involving literature data and anonymized clinical information, ethical committee approval was not required. Informed consent: Informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication. Consent to publish: The patient signed informed consent regarding publishing their data and photographs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Real-World Evidence for Ixekizumab in the Treatment of Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Axial Spondyloarthritis: Systematic Literature Review 2022-2023.Adv Ther. 2025 Sep;42(9):4224-4254. doi: 10.1007/s12325-025-03258-9. Epub 2025 Jul 17. Adv Ther. 2025. PMID: 40676380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
References
-
- Boboryko D, Olejnik-Wojciechowska J, Baranowska M et al (2024) Biological therapy for psoriatic arthritis: current state and future perspectives. Rheumatol Int 44:2711–2725. 10.1007/s00296-024-05722-1 - PubMed
-
- Toussirot E (2018) Ixekizumab: an anti-IL-17A monoclonal antibody for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis. Expert Opin Biol Ther 18(1):101–107. 10.1080/14712598.2018.1410133 - PubMed
-
- Azhar A, Zaayman M, Silfvast-Kaiser A, Kivelevitch D, Menter A, Paek SY (2020) Ixekizumab in the treatment of moderate‐to‐severe plaque psoriasis: patient adherence, satisfaction, and preferences. Dermatol Ther. 10.1111/dth.14486 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical