StrainR2 accurately deconvolutes strain-level abundances in synthetic microbial communities
- PMID: 40794845
- PMCID: PMC12377904
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaf440
StrainR2 accurately deconvolutes strain-level abundances in synthetic microbial communities
Abstract
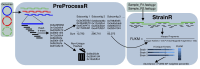
Motivation: Synthetic microbial communities offer an opportunity to conduct reductionist research in tractable model systems. However, deriving abundances of highly related strains within these communities is currently unreliable. 16S rRNA gene sequencing does not resolve abundance at the strain level and other methods such as quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) scale poorly and are resource prohibitive for complex communities. We present StrainR2, which utilizes shotgun metagenomic sequencing to provide high accuracy strain-level abundances for all members of a synthetic community, provided their genomes.
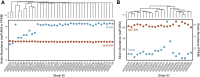
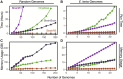
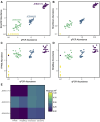
Results: Both in silico, and using sequencing data derived from gnotobiotic mice colonized with a synthetic fecal microbiota, StrainR2 resolves strain abundances with greater accuracy and efficiency than other tools utilizing shotgun metagenomic sequencing reads. We demonstrate that StrainR2's accuracy is comparable to that of qPCR on a subset of strains resolved using absolute quantification.
Availability and implementation: Software is available at GitHub and implemented in C, R, and Bash. Software is supported on Linux and MacOS, with packages available on Bioconda or as a Docker container. The source code at the time of publication is also available on figshare at the doi: 10.6084/m9.figshare.29420780.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


Update of
-
StrainR2 accurately deconvolutes strain-level abundances in synthetic microbial communities.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 9:2024.08.08.607172. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.08.607172. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Bioinformatics. 2025 Aug 2;41(8):btaf440. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaf440. PMID: 39149354 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Oshima K et al. Treg induction by a rationally selected mixture of Clostridia strains from the human microbiota. Nature 2013;500:232–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

