LRRK2-mutant microglia and neuromelanin synergize to drive dopaminergic neurodegeneration in an iPSC-based Parkinson's disease model
- PMID: 40796643
- PMCID: PMC12344146
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-08544-4
LRRK2-mutant microglia and neuromelanin synergize to drive dopaminergic neurodegeneration in an iPSC-based Parkinson's disease model
Abstract
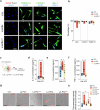
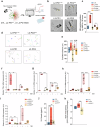
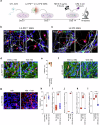
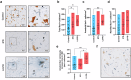
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive, incurable neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of neuromelanin (NM)-containing dopamine neurons (DAn) in the substantia nigra of the midbrain. Non-neuronal cells are increasingly recognized as contributors to PD. We generated human microglia-like cells (hMG) from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) derived from patients with LRRK2 PD-causing mutations, gene-corrected isogenic controls, and healthy donors. While neither genotype induced neurodegeneration in healthy DAn, LRRK2 hMG become hyperreactive to LPS stimulation, exhibiting increased cytokine expression, reactive oxygen species, and phagocytosis. When exposed to NM-containing particles, but not α-synuclein fibrils, LRRK2 hMG trigger DAn degeneration, in a process that is prevented by pre-treatment with the immunomodulatory drug ivermectin. Finally, post-mortem analysis of midbrain tissue of LRRK2-PD patients show increased microglia activation around NM-containing neurons, confirming our in vitro findings. Overall, our work highlights NM-activated microglia's role in PD progression, and provides a model for testing therapeutic targets.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PID2019-108792GB-I00/Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness | Agencia Estatal de Investigación (Spanish Agencia Estatal de Investigación)
- PID2022-137963OB-I00/Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness | Agencia Estatal de Investigación (Spanish Agencia Estatal de Investigación)
- 202012-32/Fundació la Marató de TV3 (TV3 Marathon Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

