TNF and type I interferon crosstalk controls the fate and function of plasmacytoid dendritic cells
- PMID: 40796660
- PMCID: PMC12396960
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-025-02234-3
TNF and type I interferon crosstalk controls the fate and function of plasmacytoid dendritic cells
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: TNF and type I interferon crosstalk controls the fate and function of plasmacytoid dendritic cells.Nat Immunol. 2025 Nov;26(11):2112. doi: 10.1038/s41590-025-02293-6. Nat Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40913098 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
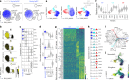
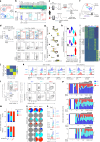
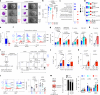
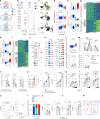
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) are major producers of type I interferon (IFN-I), an important antiviral cytokine, and activity of these cells must be tightly controlled to prevent harmful inflammation and autoimmunity. Evidence exists that one regulatory mechanism is a fate-switching process from an IFN-I-secreting pDC to a professional antigen-presenting conventional dendritic cell (cDC) that lacks IFN-I-secreting capacity. However, this differentiation process is controversial owing to limitations in tracking the fate of individual cells over time. Here we use single-cell omics and functional experiments to show that activated human pDCs can lose their identity as IFN-I-secreting cells and acquire the transcriptional, epigenetic and functional features of cDCs. This pDC fate-switching process is promoted by tumor necrosis factor but blocked by IFN-I. Importantly, it occurs in vivo during human skin inflammatory diseases and injury, and physiologically in elderly people. This work identifies the pDC-to-cDC reprogramming trajectory and unveils a mechanistic framework for harnessing it therapeutically.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: J.I. serves on the scientific advisory board of Immunitas Therapeutics; this affiliation is unrelated to the present work. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
-
- Nutt, S. L. & Chopin, M. Transcriptional networks driving dendritic cell differentiation and function. Immunity52, 942–956 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Adams, N. M., Das, A., Yun, T. J. & Reizis, B. Ontogeny and function of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol.42, 347–373 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Naik, S. H. et al. Diverse and heritable lineage imprinting of early haematopoietic progenitors. Nature496, 229–232 (2013). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AI163775/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD025212/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI158808/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI163775/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- AI158808/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

