A citrullinated histone H3 monoclonal antibody for immune modulation in sepsis
- PMID: 40796783
- PMCID: PMC12343807
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62788-6
A citrullinated histone H3 monoclonal antibody for immune modulation in sepsis
Abstract
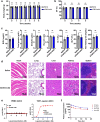
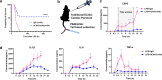
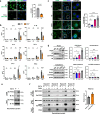
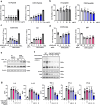
Citrullinated histone H3 (CitH3), released from immune cells during early sepsis, drives a vicious cycle of inflammation through excessive NETosis and pyroptosis, causing immune dysfunction and tissue damage. To regulate this process, we develop a humanized CitH3 monoclonal antibody (hCitH3-mAb) with high affinity and specificity to target this process. In murine models, hCitH3-mAb reduces cytokine production, mortality and acute lung injury (ALI) caused by LPS and Pseudomonas aeruginosa while enhancing bacteria phagocytosis in the lungs, spleen, and liver. Using pre-equilibrium digital ELISA (PEdELISA), we identify an optimal therapeutic window for hCitH3-mAb in sepsis-induced ALI. In parallel, we explore the molecular mechanism underlying CitH3-driven inflammation. We find that in macrophages, CitH3 activates Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), triggering Ca2+-dependent PAD2 auto-citrullination and nuclear translocation, amplifying CitH3 production via a harmful feedback loop. The hCitH3-mAb treatment effectively disrupts this cycle and restores macrophage function under septic conditions. Together, these findings highlight both the therapeutic potential of hCitH3-mAb and provide a deep mechanistic insight into the CitH3-PAD2 axis in sepsis, supporting its further development for treating immune-mediated diseases.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Patent application related to the hCitH3-mAb technology was filed by University of Virginia Patent Foundation, The Reagents of University of Michigan and HTIC, Inc. J.M., Y.L. and T.T. are co-founders of HTIC that develops hCitH3-mAb for immune modulation applications. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

