CYP1B1-AS1 regulates CYP1B1 to promote Coxiella burnetii pathogenesis by inhibiting ROS and host cell death
- PMID: 40796858
- PMCID: PMC12344041
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62762-2
CYP1B1-AS1 regulates CYP1B1 to promote Coxiella burnetii pathogenesis by inhibiting ROS and host cell death
Abstract
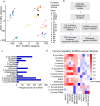
Coxiella burnetii (Cb), the causative agent of Q fever, replicates within host macrophages by modulating immune responses through poorly understood mechanisms. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are crucial yet underexplored regulators of inflammation, particularly in Cb pathogenesis. Employing a comparative transcriptomic analysis of THP-1 macrophages infected with 16 different microbes, we dissect a core set of immune-responsive lncRNAs such as MAILR, LINC01215, PACER, and MROCKI-common to human anti-pathogen responses, and distinguish them from lncRNAs specifically altered at early (1 h) time points in individual infections. In particular, our approach identifies lncRNA CYP1B1-AS1 as specifically upregulated in a spatiotemporal manner along with CYP1B1 in cis during Cb infection. Promoter assays confirm their co-regulation via a shared bidirectional promoter, while aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR)-lucia luciferase and nuclear translocation assays demonstrate that Cb infection activates AHR, driving their transcription. Knockdown of CYP1B1-AS1 or CYP1B1 alone disrupts mitochondrial homeostasis, increases ROS and mitochondrial dysfunction, and exacerbates apoptosis during infection. These findings position the CYP1B1-AS1/CYP1B1 axis as a key regulator of mitochondrial homeostasis under AHR signaling, supporting an intracellular environment that benefits Cb replication. Our results highlight the critical roles of lncRNAs in immune regulation and provide a valuable resource for future lncRNA research.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
CYP1B1-AS1 regulates CYP1B1 to promote Coxiella burnetii pathogenesis by inhibiting ROS and host cell death.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 11:rs.3.rs-5390645. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5390645/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 13;16(1):7493. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62762-2. PMID: 39711545 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Steiner, S., Meir, A. & Roy, C. R. Coxiella burnetii encodes an LvgA-related protein important for intracellular replication. Cell. Microbiol.23, e13331 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

