D-cysteine impairs tumour growth by inhibiting cysteine desulfurase NFS1
- PMID: 40797101
- PMCID: PMC12373508
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-025-01339-1
D-cysteine impairs tumour growth by inhibiting cysteine desulfurase NFS1
Abstract
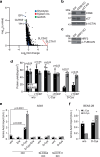
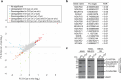
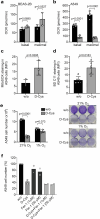
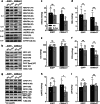
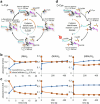
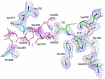
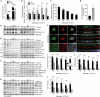
Selective targeting of cancer cells is a major challenge for cancer therapy. Many cancer cells overexpress the cystine/glutamate antiporter xCT/CD98, an L-cystine transport system that strengthens antioxidant defences, thereby promoting tumour survival and progression. Here, we show that the D-enantiomer of cysteine (D-Cys) is selectively imported into xCT/CD98-overexpressing cancer cell lines and impairs their proliferation, particularly under high oxygen concentrations. Intracellular D-Cys specifically inhibits the mitochondrial cysteine desulfurase NFS1, a key enzyme of cellular iron-sulfur protein biogenesis, by blocking sulfur mobilization due to steric constraints. NFS1 inhibition by D-Cys affects all cellular iron-sulfur cluster-dependent functions, including mitochondrial respiration, nucleotide metabolism and maintenance of genome integrity, leading to decreased oxygen consumption, DNA damage and cell cycle arrest. D-Cys administration diminishes tumour growth of human triple-negative breast cancer cells implanted orthotopically into the mouse mammary gland. Hence, D-Cys could represent a simple therapy to selectively target those forms of cancer characterized by overexpression of xCT/CD98.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: J.Z. and J.-C.M. filed a patent on the effects of d-Cys in cancer. Patent applicant: Université de Genève. Names of inventors: J.-C.M. and J.Z. Application numbers: EP 21 769 366.2 and US 18/022,824. Status of applications: pending. The patent describes the effects of d-Cys on cell proliferation in vitro and the potential of d-Cys as a therapy for tumours expressing xCT. J.-C.M. serves as an unpaid member of the scientific advisory board of MPC Therapeutics (Geneva, Switzerland). The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



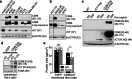
References
-
- Ohide, H., Miyoshi, Y., Maruyama, R., Hamase, K. & Konno, R. D-amino acid metabolism in mammals: biosynthesis, degradation and analytical aspects of the metabolic study. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci.879, 3162–3168 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Snyder, S. H. A life of neurotransmitters. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol.57, 1–11 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Papenbrock, J., Riemenschneider, A., Kamp, A., Schulz-Vogt, H. N. & Schmidt, A. Characterization of cysteine-degrading and H2S-releasing enzymes of higher plants - from the field to the test tube and back. Plant Biol.9, 582–588 (2007). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

