Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of Dof gene family members in mulberry trees (Morus notabilis L.) under drought stress
- PMID: 40797181
- PMCID: PMC12344836
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-025-11843-z
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of Dof gene family members in mulberry trees (Morus notabilis L.) under drought stress
Abstract
Background: The DNA-binding with one finger (Dof) gene is a classical plant transcription factor with specific conserved structural domains, which plays an important role in the regulation of plant metabolism, root development, and stress defense mechanisms. In recent years, drought has severely jeopardized the growth and development of crops and is one of the main environmental factors limiting plant growth and reducing crop yields. Whether Dof family genes play a role in mulberry drought resistance is largely unknown.
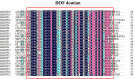
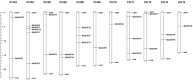
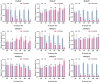
Results: To investigate the characteristics of the Dof gene family members in mulberry trees, 24 members of the mulberry Dof gene family were identified in the whole mulberry genome, and bioinformatics tools were employed to analyze the protein physicochemical properties, gene structure, phylogenetic evolution, conserved sequences, interaction networks, promoter cis-acting elements, and expression levels of Dof genes in mulberry.
Conclusions: Most of the mulberry Dof proteins were unstable, all were hydrophilic. Subcellular localization prediction showed that all proteins were localized in the nucleus. The prediction of promoter cis-elements showed that the MnDof (Morus notabilis L. Dof) gene family contained 75 promoter cis-elements for growth and development, hormone, light, and stress responses. Amino acid sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree analysis showed that all 24 Dof transcription factors contained zinc finger structural proteins. MnDof genes were distributed on all chromosomes except chromosomes 1, 2, and 7. A portion of MnDof genes responded to drought stress. These results provide information on the Dof gene family in mulberry and provide new insights into the function of MnDof genes in perennial plants, laying the foundation for further analysis of the function of these genes.
Keywords: Bioinformatics analysis; Dof transcription factor; Drought stress; Mulberry.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
[Identification of PLATZ gene family in Camellia sinensis and expression analysis of this gene family under high temperature and drought stresses].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2025 Jul 25;41(7):2897-2912. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.240969. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40769568 Chinese.
-
Genome-wide identification of Morus notabilis Aquaporin gene family and differential expression of plasma membrane intrinsic proteins in response to Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum infection.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Apr 25;25(1):531. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06541-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40281471 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide characterization of GRAS gene family and their expression profiles under diverse biotic and abiotic stresses in Amorphophallus konjac.BMC Genomics. 2025 Jul 8;26(1):643. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11777-6. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40629278 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of the DNA-Binding with One Finger Gene Family Reveals Soybean Expression Pattern and Functional Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 27;26(13):6192. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136192. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649970 Free PMC article.
-
Trihelix transcription factors are involved in drought stress response of Mangifera indica.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Aug 1;52(1):776. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10853-0. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40748574
References
-
- Blanc-Mathieu R, Dumas R, Turchi JPF. Plant-TFClass: a structural classification for plant transcription factors[J]. Trends Plant Sci. 2024;29(1):40–51. 10.1016/j.tplants.2023.06.023. - PubMed
-
- Wani SH, Anand S, Singh B, et al. WRKY transcription factors and plant defense responses: latest discoveries and future prospects [J]. Plant Cell Reports. 2021;40(7):1071–85. 10.1007/s00299-021-02691-8. - PubMed
-
- Fang XP, Wang SZ, Zhao Y, et al. Recent plant proteomics applied on biotic stress[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding. 2014;12(3):584–602.
-
- Liu L, White MJ, MacRae TH. Transcription factors and their genes in higher plants[J]. Eur J Biochem. 1999;262(2):247–57. 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00349.x. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

