Overexpression of Protein Kinase C iota as a prognostic marker and its role in oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 40797188
- PMCID: PMC12341243
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-025-04153-x
Overexpression of Protein Kinase C iota as a prognostic marker and its role in oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Protein Kinase C iota (PKCι) has been implicated in cancer progression and chemoresistance, but its prognostic significance in solid tumors remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate the expression of PKCι in tumor tissues and its association with clinicopathological features, survival outcomes, and chemotherapy response in patients with cancer.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on patients with confirmed cancer diagnoses. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was used to assess PKCι expression levels in tumor tissues. Kaplan-Meier survival curves and univariate Cox analysis were applied to evaluate the impact of PKCι expression and other clinicopathological variables on overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). The association between PKCι expression and chemotherapy resistance, particularly oxaliplatin resistance, was also investigated.
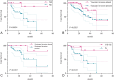
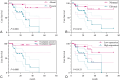
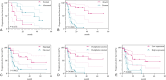
Results: PKCι overexpression was possibly correlated with advanced clinical stage, metastasis, organs involvement, vascular invasion, and perineural invasion. Patients with PKCι overexpression was possibly correlated with oxaliplatin resistance(P = 0.014). Besides, Patients with PKCι overexpression exhibited significantly shorter PFS compared to those with low expression levels (P = 0.0006). Univariate Cox analysis confirmed that metastasis (H.R. = 11.910, P = 0.018) and clinical staging (H.R. = 5.498, P = 0.027) were independent prognostic factors for OS, whereas CEA levels (H.R. = 3.497, P = 0.005) was independent predictors of PFS.
Conclusion: PKCι overexpression is associated with tumor aggressiveness and chemotherapy resistance, indicating its potential as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in cancer preliminarily.
Keywords: Cancer prognosis; Metastasis; Overall survival; Oxaliplatin resistance; PKCι; Progression-free survival; Vascular invasion.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The clinical data for this study were obtained with the approval of the Ethical Committee of The Seventh Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University. The study protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee of The Seventh Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University (approval number KY-2024-368-01) and was conducted in accordance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was not required for this study, as it was a retrospective analysis of clinical data with no ethical concerns related to human biological samples. The need for informed consent was waived by the Ethical Committee of The Seventh Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University. All procedures were performed in compliance with relevant guidelines and regulations. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
KIF2C/MCAK a prognostic biomarker and its oncogenic potential in malignant progression, and prognosis of cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis as biomarker.Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2024 Sep;61(6):404-434. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2024.2309933. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2024. PMID: 38344808 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokines as Prognostic Factor in Colorectal Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 15;25(10):5374. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105374. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791414 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer reveals a SERPINE1-based gene signature (RESIST-M) and therapeutic strategies for pro-metastatic CMS4 subtype.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Jul 16;16(1):529. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07855-y. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40664638 Free PMC article.
-
Src activity is modulated by oxaliplatin and correlates with outcomes after hepatectomy for metastatic colorectal cancer.BMC Cancer. 2014 Sep 10;14:660. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-660. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25208577 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of the C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in colorectal cancer: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2021 May 1;19(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02253-y. World J Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33933070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

