Development and validation of a Pediatric Internationally agreed UltraSound Hip synovitis protocol (PIUS-hip), by the PReS imaging working party
- PMID: 40797274
- PMCID: PMC12345126
- DOI: 10.1186/s12969-025-01134-y
Development and validation of a Pediatric Internationally agreed UltraSound Hip synovitis protocol (PIUS-hip), by the PReS imaging working party
Abstract
Background: Whilst musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSUS) normal values for examination of the hip joint have been established for healthy children, equivalent values for patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), as well as internationally validated MSUS protocols for the optimal evaluation of synovitis are lacking. This study aimed to develop and validate the most sensitive MSUS protocol for the detection of hip synovitis in JIA.
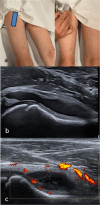
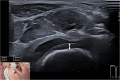
Methods: In consecutive JIA patients with ≥ 1 clinically affected hip joint, affected and unaffected hips underwent MSUS. Disease, demographic and clinical findings were recorded. Synovitis was graded using the pediatric OMERACT score for B-Mode (BM) and power-Doppler Mode (PD) in the longitudinal and transverse scans and the sensitivity and specificity was analyzed. Additionally anterior recess size (bone to capsula distance), capsula thickness and femoral head cartilage thickness (transverse view) were measured. Published data provided further control data for anterior recess size (children without JIA). Interobserver reliability of BM and PD was tested using Fleiss-Kappa.
Results: 60 patients were enrolled who had 76 hips with and 32 without clinical arthritis. BM was positive (grade ≥ 1) in 74/76 of hips with clinical arthritis (97%, sensitivity 0.97 (0.93-1.0), specificity 0.85 (0.74-0.97) versus 2/32 (6%) in hips without arthritis. PD positivity frequency was 6 (8%) in hips with arthritis versus 0 in hips without. Anterior recess size (mean ± SD) was significantly wider in patients with clinical arthritis (9.9 ± 2.5 vs 5.5 ± 1.3, p-value 0.001). Use of the cut-off of ≥ 7.2 mm resulted in an area under the curve of at least 95%, with a sensitivity of 86% and specificity of 94%. Articular capsula and femoral head cartilage thickness did not differ between patients with and without arthritis. Recess size was comparable in the internal and external control groups (n = 449). Interobserver reliability of BM and PD positivity showed excellent agreement (kappa = 0.85).
Conclusions: The Pediatric internationally agreed UltraSound hip synovitis protocol (PIUS-hip) could be limited to one longitudinal scan including B-Mode scoring plus measurement of anterior recess size for maximal sensitivity and specificity for synovitis.
Keywords: Hip synovitis; Juvenile idiopathic arthritis; Ultrasound.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Ethical approval was obtained from the ethic commissions of the University of Giessen and the Ärztekammer Westfalen-Lippe, Germany. Written patient (when aged > 6 years) and parental consent was obtained before study inclusion. Consent for publication: Consent for publication of images was obtained from patients and their legal guardians. Competing interests: This study received partial funding support from Novartis. The funding body played no role in the design of the study or in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data or in writing the manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development and validation of a pediatric internationally agreed ultrasound knee synovitis protocol (PIUS-knee) by the PReS imaging working party.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2024 Oct 21;22(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12969-024-01029-4. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2024. PMID: 39434153 Free PMC article.
-
The role of ultrasonography in assessing remission in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a systematic review.Eur J Pediatr. 2023 Jul;182(7):2989-2997. doi: 10.1007/s00431-023-04956-8. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Eur J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37117764
-
Is ultrasound a validated imaging tool for the diagnosis and management of synovitis in juvenile idiopathic arthritis? A systematic literature review.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012 Jul;64(7):1011-9. doi: 10.1002/acr.21644. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012. PMID: 22337596
-
How Is Variability in Femoral and Acetabular Version Associated With Presentation Among Young Adults With Hip Pain?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Sep 1;482(9):1565-1579. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003076. Epub 2024 May 7. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39031040 Free PMC article.
-
Which Acetabular Measurements Most Accurately Differentiate Between Patients and Controls? A Comparative Study.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Feb 1;482(2):259-274. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002768. Epub 2023 Jul 27. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 37498285 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collado P, Vojinovic J, Nieto JC, Windschall D, Magni-Manzoni S, Bruyn GAW, et al. Toward standardized musculoskeletal ultrasound in pediatric rheumatology: normal age-related ultrasound findings. Arthritis Care Res. 2016;68:348–56. - PubMed
-
- Sande NK, Kirkhus E, Lilleby V, Tomterstad AH, Aga A-B, Flatø B, et al. Validity of an ultrasonographic joint-specific scoring system in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a cross-sectional study comparing ultrasound findings of synovitis with whole-body magnetic resonance imaging and clinical assessment. RMD Open. 2024;10: e003965. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rossi-Semerano L, Breton S, Semerano L, Boubaya M, Ohanyan H, Bossert M, et al. Application of the OMERACT synovitis ultrasound scoring system in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a multicenter reliability exercise. Rheumatology. 2021;60:3579–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

