Hyperoside mitigates amphotericin B-induced nephrotoxicity in HK-2 cells via bioenergetic and oxidative stress modulation
- PMID: 40797341
- PMCID: PMC12341085
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-025-00985-1
Hyperoside mitigates amphotericin B-induced nephrotoxicity in HK-2 cells via bioenergetic and oxidative stress modulation
Abstract
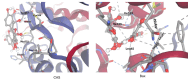
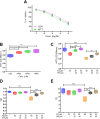
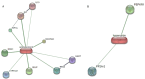
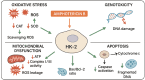
Amphotericin B (Amp-B/FZ), a first-line antifungal, is limited by dose-dependent nephrotoxicity. This study investigated the protective effects of hyperoside (HP), a dietary flavonoid, against FZ-induced renal toxicity in human proximal tubular (HK-2) cells. Molecular docking revealed strong binding affinities of HP with mitophagy (PINK1/PARKIN) and antioxidant (Nrf2/HO-1) regulators, contrasting with FZ's preferential binding to mitochondrial complex I. FZ (30-60 µM) induced cytotoxicity (MTT/LDH), genotoxicity (comet assay), and bioenergetic disruption: ATP depletion (58%), mitochondrial complex I/III inhibition (42-67%), and PINK1/PARKIN dysregulation. FZ elevated reactive species (3.2-fold) and lipid peroxidation (2.8-fold) while suppressing catalase (64%) and superoxide dismutase (51%) activities. qPCR confirmed FZ-induced downregulation of NDUFS1, CYC1, CAT, and SOD2, alongside impaired Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant signaling. Co-treatment with HP (20-40 µM) attenuated FZ toxicity, restoring ATP (1.8-fold), mitochondrial complex activities (35-49%), and antioxidant defenses (CAT:2.1-fold, SOD:1.7-fold). HP also normalized Nrf2/HO-1 expression and mitigated oxidative/genotoxic damage. These findings highlight HP's dual role in countering FZ-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, positioning it as a promising nephroprotective adjuvant. Further in vivo validation could advance HP's clinical application in reducing antifungal-associated renal injury.
Keywords: Amphotericin B; Bioenergetic disruption; Fungizone; Hyperoside; Nephrotoxicity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: Not applicable. Consent to participate: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Perazella MA. Renal vulnerability to drug toxicity. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4(7):1275–83. - PubMed
-
- Al-Khikani FHO. Amphotericin B, The wonder of today’s pharmacology science: persisting usage for more than seven decades. Pharm Biomedical Res 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

