The diagnostic and prognostic significance of methylated arginine metabolites (ADMA, SDMA, L-NMMA) in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
- PMID: 40797410
- PMCID: PMC12338228
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043903
The diagnostic and prognostic significance of methylated arginine metabolites (ADMA, SDMA, L-NMMA) in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
Abstract
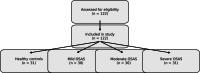
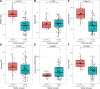
In obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS), changes in the levels of methylated arginine derivatives have been observed due to intermittent hypoxia. While intermittent hypoxia initially increases the activity of the enzyme dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase (DDAH), thereby reducing the levels of methylated arginine derivatives, prolonged hypoxia can disrupt this mechanism and trigger vascular damage. Therefore, methylated arginine metabolites play a critical role in the pathophysiology of OSAS. This study investigates the relationship between the L-arginine-nitric oxide (NO) pathway and methylated arginine metabolites-asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA), and N-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA)-in newly diagnosed OSAS patients without comorbidities, aiming to evaluate their potential as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. This observational case-control study included a total of 122 participants, consisting of 31 healthy controls and 91 patients with OSAS. OSAS patients were stratified by disease severity into 30 mild, 30 moderate, and 31 severe cases. Serum levels of methylated arginine metabolites (ADMA, SDMA, and L-NMMA) and arginine were measured using mass spectrometry. The analyses were performed with an AB Sciex API 3200 triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (USA) equipped with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source operating in positive ion mode, coupled to a Shimadzu LC-20AD liquid chromatography system (Kyoto, Japan). Compared to the control group, OSAS patients showed statistically significant lower levels of ADMA, L-NMMA, arginine, and total methylated arginine load (TMAL) (P < .001). SDMA levels were similar across groups. In OSAS patients without comorbidities, a reduction in TMAL may suggest the activation of compensatory mechanisms in response to sleep-related intermittent hypoxia. This could reflect a shift in the arginine pathway towards enhanced nitric oxide synthesis to mitigate hypoxia-induced vasoconstriction through vasodilation. The reduced arginine levels are likely due to increased utilization, while diminished synthesis of methylated arginine derivatives (ADMA, L-NMMA) may result from this metabolic shift. These findings imply that decreased arginine and methylated arginine levels may serve as potential diagnostic markers and could aid in identifying candidates for polysomnography (PSG), which is both costly and time-consuming, thereby contributing to more efficient patient selection and reducing the overall clinical burden.
Keywords: ADMA; L-NMMA; NO; OSAS; SDMA; TMAL; intermittent hypoxia.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Tonsillectomy or adenotonsillectomy versus non-surgical management for obstructive sleep-disordered breathing in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 14;2015(10):CD011165. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011165.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26465274 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Plasma levels of NO-related pathway molecules to predict post-transcatheter aortic valve implantation major adverse cardiovascular events: a prospective, multicenter study.Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. 2025 Jun 4;21(2):211-220. doi: 10.5114/aic.2025.151798. eCollection 2025 Jun. Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. 2025. PMID: 40656163 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Uremic Solutes With Cardiovascular Death in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Am J Kidney Dis. 2022 Oct;80(4):502-512.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2022.02.016. Epub 2022 Mar 26. Am J Kidney Dis. 2022. PMID: 35351578 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

