Association between 20 medications and erectile dysfunction: Results from a cross-sectional study and Mendelian randomization analysis
- PMID: 40797411
- PMCID: PMC12338166
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043157
Association between 20 medications and erectile dysfunction: Results from a cross-sectional study and Mendelian randomization analysis
Abstract
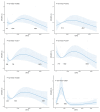
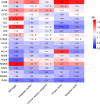
Previous studies on the impact of medication use on the risk of erectile dysfunction (ED) have yielded controversial results. Therefore, this study aims to explore the association between the use of 20 different drugs and the risk of ED through cross-sectional research and Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis. We analyzed 3989 participants from the 2001 to 2004 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Weighted multivariable logistic regression was used to analyze the association between medication use and the risk of ED. After propensity score matching, the association between the use of 20 different medications and the risk of ED was further assessed. Weighted restricted cubic splines were applied to evaluate the nonlinear relationship between the days of medication use and the risk of ED. Then, two-sample MR analysis was conducted to investigate the causal association between medication use and the risk of ED, with inverse variance weighting as the primary analytical method. Cross-sectional findings indicated salicylic acid derivatives (OR 3.28; 95% CI 1.27-8.50) and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG CoA) reductase inhibitors (OR 1.34; 95% CI 1.01-1.79) were associated with higher ED risk, and that the duration of HMG CoA reductase inhibitor use had an S-shaped nonlinear relationship with ED risk (P = .0329). The results in the preliminary MR analysis further demonstrated a causal relationship between the use of salicylic acid (OR 1.23; 95% CI 1.00, 1.51) and derivatives or HMG CoA reductase inhibitors (OR 1.12; 95% CI 1.04, 1.21) and the increased risk of ED. The meta-analysis of the preliminary MR analysis and the validation analysis also confirmed this causal relationship. Our study suggests a causal association between the use of salicylic acid and derivatives or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and an increased risk of ED. Therefore, special caution should be exercised in applying these 2 classes of drugs to patients at high risk of ED or those already suffering from ED.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; NHANES; cross-sectional study; erectile dysfunction; medication use.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Increased walking pace reduces the rate of erectile dysfunction: results from a multivariable Mendelian randomization study.J Sex Med. 2025 Jan 9;22(2):298-306. doi: 10.1093/jsxmed/qdae178. J Sex Med. 2025. PMID: 39664004
-
Association Between Opioid Use and Risk of Erectile Dysfunction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Sex Med. 2017 Oct;14(10):1209-1219. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2017.08.010. Epub 2017 Sep 8. J Sex Med. 2017. PMID: 28923307
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
To explore the association between the neutrophil percentage to albumin ratio and low bone mineral density/osteoporosis based on NHANES 2011-2018.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 12;15(1):29544. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12732-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40796591 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shamloul R, Ghanem H. Erectile dysfunction. Lancet (London, England). 2013;381:153–65. - PubMed
-
- Muneer A, Kalsi J, Nazareth I, Arya M. Erectile dysfunction. BMJ. 2014;348:g129. - PubMed
-
- Xiong Y, Zhang Y, Zhang F, Wu C, Qin F, Yuan J. Applications of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and prediction of erectile dysfunction: a narrative review. Int J Impot Res. 2023;35:95–102. - PubMed
-
- Korfage IJ, Pluijm S, Roobol M, Dohle GR, Schröder FH, Essink-Bot ML. Erectile dysfunction and mental health in a general population of older men. J Sex Med. 2009;6:505–12. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

