Dissecting causal networks of inflammatory factors and metabolites in heart failure: A mediation Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 40797443
- PMCID: PMC12338296
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043801
Dissecting causal networks of inflammatory factors and metabolites in heart failure: A mediation Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
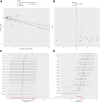
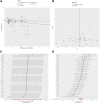
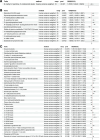
Heart failure (HF) represents a major global health burden, with complex pathophysiology involving inflammatory and metabolic pathways. However, the causal relationships among inflammatory factors, metabolites, and HF risk remain unclear. This study aims to identify inflammatory factors causally associated with HF risk, characterize metabolic alterations causally linked to HF development, and explore potential mediating roles of metabolites in inflammation-related HF pathogenesis. We conducted a comprehensive Mendelian randomization study using genetic data from FinnGen biobank (29,218 HF cases and 381,838 controls), combined with genome-wide association studies data for 91 inflammatory factors and 1400 metabolites. We performed bidirectional and mediational Mendelian randomization analyses to investigate causal relationships and potential mediating effects of metabolites in inflammation-related HF pathogenesis. We identified 9 inflammatory factors (out of 91) causally associated with HF risk, including 3 risk-promoting factors (interferon gamma: OR = 1.080, matrix metalloproteinase-1: OR = 1.081, tumor necrosis factor-beta: OR = 1.064) and 6 protective factors (CD40L receptor: OR = 0.954, DNER: OR = 0.943, IL-10: OR = 0.950, LIFR: OR = 0.911, TNFSF12: OR = 0.933, uPA: OR = 0.927). More than 13 metabolites (out of 1400) showed robust associations with HF risk, with N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide demonstrating the strongest evidence (OR = 1.058). Further analysis revealed 23 significant inflammatory factor-metabolite pairs (out of 1000s of possible combinations), suggesting potential mechanistic pathways through which inflammatory factors influence HF development. This study establishes a comprehensive causal framework linking inflammation to HF through specific metabolic alterations, identifying novel biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets. The findings suggest that combined interventions targeting both inflammatory and metabolic pathways might offer improved strategies for HF prevention and treatment.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization; blood metabolites; heart failure; inflammatory factors; mediation analysis; precision medicine.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Integrative analysis reveals novel inflammatory and metabolic pathways in glioblastoma development: A large-scale mediation Mendelian randomization study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Aug 1;104(31):e43636. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043636. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40760641 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiota causally affects ulcerative colitis by potential mediation of plasma metabolites: A Mendelian randomization study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jun 27;104(26):e42791. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042791. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40587710 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic prediction of immune cells, inflammatory proteins, and metabolite-mediated association between gut microbiota and COPD: a Mendelian randomization study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21633. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05290-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594427 Free PMC article.
-
Multiomics insight into the role of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in heart failure.ESC Heart Fail. 2025 Aug;12(4):2958-2968. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.15310. Epub 2025 Apr 28. ESC Heart Fail. 2025. PMID: 40290076 Free PMC article.
-
Insights from Mendelian randomization and genetic correlation analyses into the relationship between endometriosis and its comorbidities.Hum Reprod Update. 2023 Sep 5;29(5):655-674. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmad009. Hum Reprod Update. 2023. PMID: 37159502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Khan MS, Shahid I, Bennis A, Rakisheva A, Metra M, Butler J. Global epidemiology of heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024;21:717–34. - PubMed
-
- Zhang JJ, Pogwizd SM, Fukuda K, et al. Trials and tribulations of cell therapy for heart failure: an update on ongoing trials. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024;22:372–85. - PubMed
-
- Cook C, Cole G, Asaria P, Jabbour R, Francis DP. The annual global economic burden of heart failure. Int J Cardiol. 2014;171:368–76. - PubMed
-
- Ajoolabady A, Pratico D, Vinciguerra M, Lip GYH, Franceschi C, Ren J. Inflammaging: mechanisms and role in the cardiac and vasculature. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2023;34:373–87. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

