Comparison of analgesic efficacy, anti-inflammatory effect, and myotoxicity of ultrasound-guided suprainguinal fascia iliaca block and adductor canal with IPACK combination in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty under spinal anesthesia: A prospective observational study
- PMID: 40797488
- PMCID: PMC12338259
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043719
Comparison of analgesic efficacy, anti-inflammatory effect, and myotoxicity of ultrasound-guided suprainguinal fascia iliaca block and adductor canal with IPACK combination in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty under spinal anesthesia: A prospective observational study
Abstract
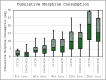
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is associated with significant postoperative pain, managed with multimodal analgesia, including regional anesthesia techniques like peripheral nerve blocks. The knee joint's innervation by both sacral and lumbar plexuses often necessitates combined blocks for effective analgesia. This study aimed to compare the effects of suprainguinal fascia iliaca block (SIFIB) and a combination of popliteal artery and posterior knee capsule injection (IPACK) with adductor canal block (ACB) on 24-hour postoperative pain scores, as well as their impact on inflammatory markers and biochemical indicators of myotoxicity. The study included patients undergoing elective unilateral primary knee arthroplasty. They were divided into 2 groups: 1 received postoperative SIFIB, and the other underwent IPACK preoperatively and ACB postoperatively. Postoperative evaluations included Numeric Rating Scale scores, morphine consumption, quadriceps muscle strength, neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet/lymphocyte ratio (PLR), systemic immune inflammation score, C-reactive protein (CRP), lactate, and creatine phosphokinase (CPK) levels as a marker of myotoxicity. CPK increases of more than 5-fold were assessed for rhabdomyolysis. Pain scores at rest and with movement were comparable between groups at all time points (P > .05). Morphine consumption over 24 hours did not differ significantly (P > .05). Similarly, inflammatory markers, including NLR, PLR, systemic immune inflammation score, CRP, and lactate, showed no significant differences between groups at 12 and 24 hours (P > .05). CPK levels, evaluated as indicators of myotoxicity and rhabdomyolysis, were also similar (P > .05). Quadriceps strength, assessed as an indicator of motor loss, showed no significant differences between groups (P > .05). The analgesic efficacy, safety, and inflammatory responses of SIFIB were comparable to those of the IPACK + ACB combination. Given its technical simplicity and ability to target multiple nerves with a single injection, SIFIB may be considered a practical alternative for postoperative analgesia in TKA. These findings may assist clinicians in selecting regional anesthesia strategies when procedural limitations exist.
Keywords: adductor canal block; numerical pain scores; posterior knee capsule local anesthetic injection; suprainguinal fascia iliaca block; total knee arthroplasty.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Albrecht E, Wegrzyn J, Dabetic A, El-Boghdadly K. The analgesic efficacy of iPACK after knee surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. J Clin Anesth. 2021;72:110305. - PubMed
-
- Lavand’homme PM, Kehlet H, Rawal N, Joshi GP; PROSPECT Working Group of the European Society of Regional Anaesthesia and Pain Therapy (ESRA). Pain management after total knee arthroplasty: PROcedure SPEcific postoperative pain ManagemenT recommendations. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2022;39:743–57. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

