How much can children see and report about their experience of a brief glance at a natural scene?
- PMID: 40799209
- PMCID: PMC12342378
- DOI: 10.1093/nc/niaf019
How much can children see and report about their experience of a brief glance at a natural scene?
Abstract
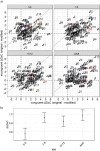
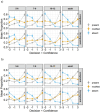
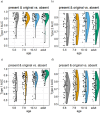
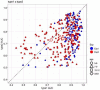
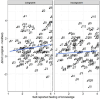
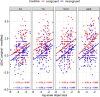
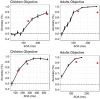
Recent studies on brief scene perception have revealed that adults discriminate between what they see and do not see in a photograph with varying degrees of confidence. In this study, we attempt to extend previous studies by asking if these perceptual/cognitive abilities are already established in preschool and school-aged children. In Experiment 1 (n = 122) and 2 (n = 205, registered report), using an online experiment, we briefly presented a natural scene (267 ms in Experiment 1 and 133 ms in Experiment 2) to participants and, subsequently, asked them if a small patch was included in the original scene. Experiment 2 was a registered report. We tested various patch locations to probe "how much" the participants can see and report about it with graded levels of confidence. In Experiment 1, discriminative performance was nearly saturated (the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC)) = 0.9 across age groups) with no effects of ages, but metacognition slightly improved across ages (AUC = 0.74 in 5-6-year-olds to 0.79 in adults). In a critical registered report (Experiment 2), with reduced stimulus duration, we found a developmental effect (AUC = 0.73 in 5-6-year-olds to 0.91 in adults), and, again, metacognitive accuracy was constant across development (AUC = 0.73 in 5-6-year-olds to 0.75 in adults). Additionally, our analysis of semantic congruence between objects and scenes revealed age-related differences in performance. Contrary to our expectation, the size of the image modification strongly affected task performance, uniformly across ages. Overall, we conclude that 5-6-year-olds' perceptual and metacognitive abilities are much better than we expected when they were tested with briefly presented natural scenes, although their performances were generally lower than adults.
Keywords: children; cognitive development; massive report paradigm; metacognition; natural scene perception; visual experience.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Adapting Safety Plans for Autistic Adults with Involvement from the Autism Community.Autism Adulthood. 2025 May 28;7(3):293-302. doi: 10.1089/aut.2023.0124. eCollection 2025 Jun. Autism Adulthood. 2025. PMID: 40539213
-
"In a State of Flow": A Qualitative Examination of Autistic Adults' Phenomenological Experiences of Task Immersion.Autism Adulthood. 2024 Sep 16;6(3):362-373. doi: 10.1089/aut.2023.0032. eCollection 2024 Sep. Autism Adulthood. 2024. PMID: 39371355
-
How lived experiences of illness trajectories, burdens of treatment, and social inequalities shape service user and caregiver participation in health and social care: a theory-informed qualitative evidence synthesis.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025 Jun;13(24):1-120. doi: 10.3310/HGTQ8159. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025. PMID: 40548558
-
Digital interventions in mental health: evidence syntheses and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Jan;26(1):1-182. doi: 10.3310/RCTI6942. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 35048909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baer C, Gill IK, Odic D. A domain-general sense of confidence in children. Open Mind 2018;2:86–96. 10.1162/opmi_a_00020 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
