RNLS promotes ovarian cancer growth and inhibits ferroptosis via mediating STAT3
- PMID: 40799250
- PMCID: PMC12339330
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1604377
RNLS promotes ovarian cancer growth and inhibits ferroptosis via mediating STAT3
Abstract
Introduction: Ovarian cancer (OC) is a lethal malignancy for which there are limited therapeutic options. The role of renalase (RNLS) in cancer progression and ferroptosis regulation remains unclear. This study investigates how RNLS mediates STAT3 to promote OC growth and suppress ferroptosis.
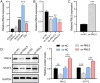
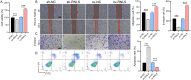
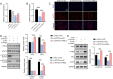
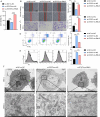
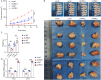
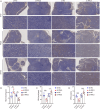
Methods: RNLS expression was analyzed in OC cell lines (OVCAR3) and normal ovarian epithelial cells (IOSE80) via qPCR. Stable RNLS knockdown (sh-RNLS) and overexpression (ov-RNLS) OVCAR3 models were established via lentiviral infection. STAT3 siRNA was transfected to explore RNLS-STAT3 interactions. Functional assays (CCK8, wound healing, Transwell, flow cytometry) evaluated proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis, and ROS levels. Mitochondrial morphology was assessed by electron microscopy. Subcutaneous tumor models in mice validated in vivo effects. Molecular markers (STAT3, p-PI3K/PI3K, p-AKT/AKT, Ki-67, MDA, GPX4, GSH) were analyzed via Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA.
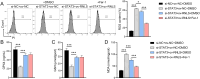
Results: RNLS was significantly upregulated in OC cells, particularly OVCAR3. RNLS knockdown suppressed STAT3 expression, cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and tumor growth, while promoting apoptosis, ROS accumulation, and mitochondrial damage. Conversely, RNLS overexpression exerted opposing effects. STAT3 silencing inhibited PI3K/AKT signaling and ferroptosis resistance, which were rescued by RNLS overexpression. In vivo, sh-RNLS reduced tumor volume/weight, as well as RNLS/STAT3, Ki-67, GPX4, and GSH, while increasing MDA. ov-RNLS enhanced tumor growth and reversed these molecular changes.
Conclusion: RNLS drives OC progression by activating STAT3-dependent PI3K/AKT signaling, enhancing proliferation, metastasis, and ferroptosis suppression. Targeting RNLS-STAT3 axis may offer a novel therapeutic strategy against OC.
Keywords: PI3K/AKT; RNLS; STAT3; ovarian cancer; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2025 Lin, Xie, Zhong, Chen, Ma, Li, Chen and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Caveolin-1 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma via EGFR degradation.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21654. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05259-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594106 Free PMC article.
-
Aldo-keto Reductase 1B10 (AKR1B10) Suppresses Sensitivity of Ferroptosis in TNBC by Activating the AKT/GSK3β/Nrf2/GPX4 Axis.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2025 Jun 27;30(6):36615. doi: 10.31083/FBL36615. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2025. PMID: 40613296
-
Integrin αVβ1-activated PYK2 promotes the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer via the STAT3-VGF axis.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jun 6;22(1):313. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01639-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38844957 Free PMC article.
-
UCHL3 regulates snail stability and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer.Cytotechnology. 2025 Aug;77(4):152. doi: 10.1007/s10616-025-00811-w. Epub 2025 Jul 18. Cytotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40689350
-
The mechanism of lncRNA SSTR5-AS1 promoting ferroptosis resistance and immune escape in ovarian cancer cells by recruiting STAT3 to regulate SLC7A11 expression.Cancer Genet. 2025 Jul 16;296-297:172-181. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2025.07.009. Online ahead of print. Cancer Genet. 2025. PMID: 40716132
References
-
- Ferri-Borgogno S, Zhu Y, Sheng J, Burks JK, Gomez JA, Wong KK, et al. Spatial transcriptomics depict ligand-receptor cross-talk heterogeneity at the tumor-stroma interface in long-term ovarian cancer survivors. Cancer Res. (2023) 83:1503–16. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-1821, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

