Association of cholesterol and triglyceride levels with the recurrence of early-stage lung adenocarcinoma with micropapillary pattern
- PMID: 40799430
- PMCID: PMC12337042
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-2025-118
Association of cholesterol and triglyceride levels with the recurrence of early-stage lung adenocarcinoma with micropapillary pattern
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer remains the predominant cause of cancer-related mortality, with adenocarcinoma being the most prevalent histological subtype. Within our nation, lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) exhibits the highest incidence and mortality rates among all malignant neoplasms. Specifically, the micropapillary subtype of adenocarcinoma is characterized by particularly poor prognosis and significantly reduced survival rate. Accumulated evidence from prior investigations has identified the micropapillary subtype of LUAD as a high-risk factor for distant metastasis and local recurrence. Nevertheless, the precise correlation between postoperative alterations in cholesterol levels, triglyceride levels and the prognosis of patients with micropapillary LUAD remains to be elucidated. This study aimed to the identify factors influencing postoperative metastatic and recurrence in patients with LUAD with micropapillary pattern (MPP).
Methods: A retrospective analysis of 261 patients with MPP and 658 without MPP was conducted, with postoperative pathological analysis determining the MPP. The patients were divided into recurrence (n=58) and non-recurrence (n=203) groups. Postoperative pathological analysis determined the content of micropapillary components in each LUAD case. Patients were categorized into a positive recurrence group (n=58) and a negative recurrence group (n=203). Univariate analyses, logistic multivariate analyses, and survival analyses were performed on the clinical data.
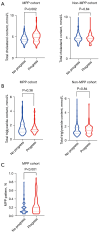
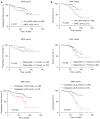
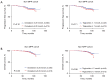
Results: Univariate and multivariate analyses revealed that high MPP, tumor size, and abnormal total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride levels were independent risk factors for recurrence in patients with MPP but not in patients of pattern without it. Survival analysis showed that abnormal cholesterol and triglyceride levels are risk factors for a poor prognosis in patients with MPP. Additionally, a scoring system was developed to identify high-risk patients among those with MPP.
Conclusions: Abnormal cholesterol levels and abnormal triglyceride levels are high-risk factors for postoperative recurrence and metastasis in patients with LUAD containing micropapillary components. However, for patients with LUAD that does not contain micropapillary components in the postoperative pathology, there is no significant correlation between prognosis and abnormal cholesterol levels or triglyceride levels.
Keywords: Micropapillary; lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD); metastasis; total cholesterol (TC); total triglyceride.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-2025-118/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
