Analyzing RNA Localization Using the RNA Proximity Labeling Method OINC-seq
- PMID: 40799472
- PMCID: PMC12336859
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5403
Analyzing RNA Localization Using the RNA Proximity Labeling Method OINC-seq
Abstract
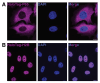
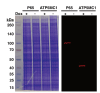
Thousands of RNAs are localized to specific subcellular locations, and these localization patterns are often required for optimal cell function. However, the sequences within RNAs that direct their transport are unknown for almost all localized transcripts. Similarly, the RNA content of most subcellular locations remains unknown. To facilitate the study of subcellular transcriptomes, we developed the RNA proximity labeling method OINC-seq. OINC-seq utilizes photoactivatable, spatially restricted RNA oxidation to specifically label RNA in proximity to a subcellularly localized bait protein. After labeling, these oxidative RNA marks are then read out via high-throughput sequencing due to their ability to induce predictable misincorporation events by reverse transcriptase. These induced mutations are then quantitatively assessed for each gene using our software package PIGPEN. The observed mutation rate for a given RNA species is therefore related to its proximity to the localized bait protein. This protocol describes procedures for assaying RNA localization via OINC-seq experiments as well as computational procedures for analyzing the resulting data using PIGPEN. Key features • OINC-seq assays the RNA content of a variety of subcellular locations. • OINC-seq utilizes a photoactivatable, proximity-dependent RNA oxidation reaction to label RNAs. • Oxidative RNA marks are read using high-throughput sequencing without the need for enrichment. • Oxidative RNA marks are identified and quantified using the associated PIGPEN software.
Keywords: Proximity labeling; RNA localization; RNA modifications; RNA oxidation; RNA trafficking.
©Copyright : © 2025 The Authors; This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Goering R., Hudish L. I., Guzman B. B., Raj N., Bassell G. J., Russ H. A., Dominguez D. and Taliaferro J. M.(2020). FMRP promotes RNA localization to neuronal projections through interactions between its RGG domain and G-quadruplex RNA sequences. eLife. 9: e52621. https://doi.org/ 10.7554/elife.52621 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

