The Prognostic Value of B12/CRP Ratio (BCR) in Patients Diagnosed With Solid Cancer
- PMID: 40799500
- PMCID: PMC12340191
- DOI: 10.1177/11795549251360891
The Prognostic Value of B12/CRP Ratio (BCR) in Patients Diagnosed With Solid Cancer
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to determine the prognostic effect of the serum vitamin B12 level/CRP ratio (BCR) on patients diagnosed with solid cancer.
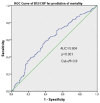
Methods: Patients >18 years diagnosed with solid cancer were included in the study, the data of the patients were retrospectively examined, and the cut-off values for BCR were determined using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. Accordingly, grouping was performed, appropriate statistical analyses were performed, and P < .05 was accepted as the significance limit value.
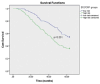
Results: The median age of the 344 patients included in the study was found to be 60.9 (range: 27-88) years. Around 56.6% (n = 174) of the patients had nondistant metastatic group and 49.4% (n = 170) had metastatic group. The median follow-up period of the patients was found to be 46.8 (range: 4-63) months. In the metastatic group, mortality was statistically significantly 2.1 times higher in those with a BCR cut-off value <3.5 (95% confidence interval [CI]; 1.4-3.2, P < .001). In the nonmetastatic group, mortality was statistically significantly twice higher in those with a BCR cut-off value <3.8 (95% CI; 1.4-3.3, P < .001). In addition, mortality was statistically significantly higher in high-risk patients in the nonmetastatic group (63.8% (n = 188) vs 45.5% (n = 156) (P < .001). The mOS period for patients in the high-risk group was 42.8 ± 1.4 (95% CI: 40.1-45.5) months, the mOS period for patients in the low-risk group was 51.5 ± 1.3 (95% CI: 49.0-54.0) months, and the mOS period for the entire group was 46.8 ± 1.0 (95% CI: 44.8-48.7) months (P < .001).
Conclusıons: In conclusion, our study has shown that BCR, which has not been reported in the literature to date, is one of the cheapest and easily accessible inflammation markers that can determine prognosis in cancer patients.
Keywords: B12/CRP Ratio (BCR); prognostic factors; solid cancer.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous