Diabetes-preventive molecular mechanisms of breast versus formula feeding: new insights into the impact of milk on stem cell Wnt signaling
- PMID: 40799516
- PMCID: PMC12341479
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1652297
Diabetes-preventive molecular mechanisms of breast versus formula feeding: new insights into the impact of milk on stem cell Wnt signaling
Abstract
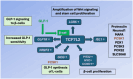
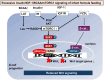
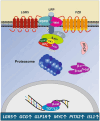
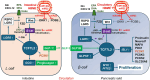
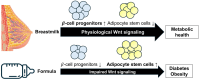
Human milk serves as a transmitter for epigenetic programming involved in postnatal tissue development and organ maturation of the infant. In contrast to formula feeding (FF), prolonged breastfeeding (BF) has been associated with diabetes-preventive effects. Polymorphisms of the transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2), the key downstream effector of Wingless (Wnt) signaling, increase the risk of diabetes mellitus. Wnt signaling is crucial for β-cell development and proliferation. However, there is limited information regarding Wnt/β-catenin/TCF7L2-dependent effects of BF versus FF on postnatal β-cell progenitor cell development, β-cell proliferation and β-cell mass expansion. The objective of our literature review is to collect and analyze data to provide translational evidence that different components of human milk promote Wnt signaling. We will specifically focus on the variations in Wnt signaling in enteroendocrine L-cells and pancreatic β-cells in response to either FF or BF. FF-induced overstimulation of mTORC1 may suppress Wnt gene expression through S6K1-mediated histone H3K27 trimethylation (H3K27me3). Moreover, the absence of milk exosomal miRNAs in formula that target mRNAs of crucial Wnt inhibitors, as well as reduced levels of eicosapentaenoic acid and glutamine in formula, may further hinder appropriate Wnt signaling, negatively impacting intestinal stem cells, enteroendocrine L-cells and potentially β-cell progenitor cells. Overall, the evidence presented supports the conclusion that FF has a detrimental impact on the Wnt/β-catenin/TCF7L2-regulated enteroendocrine-islet axis, disrupting proper β-cell maturation and proliferation. We propose that human milk, compared to formula, offers optimized conditions for physiological Wnt signaling promoting adequate neonatal β-cell mass expansion, which could explain the early diabetes-preventive effects of prolonged BF.
Keywords: breastfeeding; diabetes mellitus; diabetes prevention; formula feeding; microRNA; milk exosome; wingless signaling; β-cell.
Copyright © 2025 Melnik, Weiskirchen, Weiskirchen, Stremmel, John, Leitzmann and Schmitz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

