This is a preprint.
Genetic mechanisms of resistance to targeted KRAS inhibition
- PMID: 40799582
- PMCID: PMC12340830
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.08.04.668444
Genetic mechanisms of resistance to targeted KRAS inhibition
Abstract
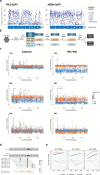
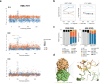
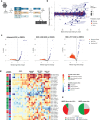
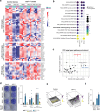
KRAS mutations are among the most prevalent oncogenic drivers in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), yet the mechanisms of therapeutic resistance to KRAS inhibitors in these cancers remains poorly understood. Here, we deploy high-throughput CRISPR base editing screens to systematically map resistance mutations to three mechanistically distinct KRAS-targeted therapies, including KRAS-G12C(OFF) inhibitor (adagrasib), RAS(ON) G12C-selective tri-complex inhibitor (RMC-4998), and RAS(ON) multi-selective tri-complex inhibitor (RMC-7977). Using both a saturation Kras tiling approach and cancer-associated mutation library, we identify common and compound-selective second-site resistance mutations in Kras, as well as gain-of-function and loss-of-function variants across cancer-associated genes that rewire signaling networks in a context-dependent manner. Notably, we identify a recurrent missense mutation in capicua (Cic), that promotes resistance to RMC-7977 in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, we show that targeting NFκB signaling in CIC-mutant cells can resensitize them to RAS pathway inhibition and overcome resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement LED is a consultant for and holds equity in Mirimus Inc., unrelated to this work. LED is a consultant for and has received grant funding from Revolution Medicines, Inc. related to this work. AT, NAV, AK, MPL, IA, and MS are employees and stockholders of Revolution Medicines, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Society, A. C. Facts & Figures 2025, <https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/lung-cancer/about/key-statistics.html> (2025).
-
- Christensen J. G. et al. The KRASG12C Inhibitor, MRTX849, Provides Insight Toward Therapeutic Susceptibility of KRAS Mutant Cancers in Mouse Models and Patients. Cancer Discovery, CD-19–1167 (2019). 10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-19-1167 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
