Gut microbiome dysregulation in noninfectious uveitis
- PMID: 40799652
- PMCID: PMC12339559
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1614304
Gut microbiome dysregulation in noninfectious uveitis
Abstract
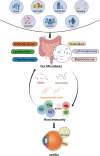
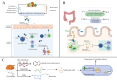
Noninfectious uveitis (NIU) is a vision-threatening autoimmune disease of the eye, but its pathogenesis is still not fully understood. Recently, accumulating evidence suggests that gut microbiome dysbiosis may affect the development and progression of NIU through potential mechanisms, including translocation, molecular mimicry, and bystander activation. Understanding the mechanisms of gut microbiome-host interactions, especially the gut-eye axis regulation, can offer a theoretical foundation for developing novel therapeutic strategies. We summarized current evidence on the dysregulation of gut microbiome and metabolites in NIU, and explored potential mechanisms involved. Furthermore, possible therapeutic measures are discussed, including probiotics, prebiotics, dietary modifications, antibiotic interventions, as well as fecal microbial transplantation, aiming to exert beneficial effects on NIU progression by reshaping the gut microbial composition.
Keywords: T helper 1/17 cell; T regulatory cells; dysregulation; gut microbiome; gut-eye axis; noninfectious uveitis; treatment intervention.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Geng, Liu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

