Cardiovascular effects on high-resolution 3D multi-shot diffusion MRI of the rhesus macaque brain
- PMID: 40799687
- PMCID: PMC12007547
- DOI: 10.1162/imag_a_00039
Cardiovascular effects on high-resolution 3D multi-shot diffusion MRI of the rhesus macaque brain
Abstract
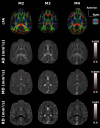
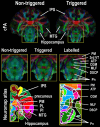
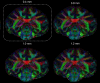
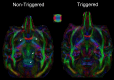
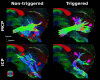
The monkey brain represents a key research model thanks to its strong homologies with the humans, but diffusion-MRI (dMRI) performed at millimeter-level resolution using clinical scanners and pulse-sequences cannot take full advantage of this. Cardiovascular effects on 3D multi-shot Echo-Planar Imaging (3D-msEPI) dMRI were characterized at submillimetric resolution by comparing triggered and non-triggered diffusion-weighted (DW)-images and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) maps. We also investigated the value of 3D-msEPI with cardiovascular-triggering to achieve dMRI of the anesthetized macaque brain with high resolution previously restricted to ex-vivo brains. Eight DW-images with voxel-size = 0.5 × 0.5 × 1 mm3 and b = 1500 s/mm2 were collected at 3 Tesla from two macaques using triggered and then non-triggered 3D-msEPI. Statistical analysis by mixed models was used to compare signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and ghost-to-signal ratio (GSR) of DW-images with and without triggering. Brain DTI with isotropic-resolution of 0.4 mm and b = 1000 s/mm2 was also collected in three macaques with triggered 3D-msEPI and reapplied without triggering in one. Cardiovascular pulsations induce inter-shot phase-errors with non-linear spatial dependency on DW-images, resulting in ghost-artifacts and signal loss particularly in the brainstem, thalamus, and cerebellum. Cardiovascular-triggering proved effective in addressing these, recovering SNR in white and gray matter (all p < 0.0001), and reducing GSR from 16.5 ± 10% to 4.7 ± 4.2% on DW-images (p < 0.0001). Triggered 3D-msEPI provided DTI-maps with the unprecedented spatial-resolution of 0.4 mm, enabling several substructures of the macaque brain to be discerned and thus analyzed in vivo. The value of cardiovascular-triggering in maintaining DTI-map sharpness and guaranteeing accurate tractography results in the brainstem, thalamus, and cerebellum was also demonstrated. In conclusion, this work highlights the effects of cardiovascular pulsations on brain 3D-dMRI and the value of triggered 3D-msEPI to provide high-quality diffusion-MRI of the anesthetized macaque brain. For routine studies, 3D-msEPI must be coupled with appropriate techniques to reduce acquisition duration.
Keywords: 3D multi-shot EPI; cardiovascular effect; diffusion MRI; high-resolution brain imaging; macaque brain; triggered diffusion MRI.
© 2023 Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
T.T. is a Siemens Healthineers employee supporting MRI research customers for scientific and clinical developments. He is involved in the project referred to this manuscript as he supports the project for the MRI sequence developed in-house as well as the MR protocol setup. All other authors (Y.B.-P., S.T., H.R., M.F., F.L., Z.Z., M.G., N.R., S.B.H., and B.H.) declare having no competing financial and/or non-financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Alhamud, A., Taylor, P. A., Van Der Kouwe, A. J. W., & Meintjes, E. M. (2016). Real-time measurement and correction of both B0 changes and subject motion in diffusion tensor imaging using a double volumetric navigated (DvNav) sequence. NeuroImage, 126, 60–71. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.11.022 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atkinson, D., Porter, D. A., Hill, D. L. G., Calamante, F., & Connelly, A. (2000). Sampling and reconstruction effects due to motion in diffusion-weighted interleaved echo planar imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 44(1), 101–109. 10.1002/1522-2594(200007)44:1<101::AID-MRM15>3.0.CO;2-S - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
