Unique information from common diffusion MRI models about white-matter differences across the human adult lifespan
- PMID: 40799710
- PMCID: PMC12327084
- DOI: 10.1162/imag_a_00051
Unique information from common diffusion MRI models about white-matter differences across the human adult lifespan
Abstract
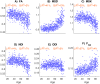
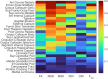
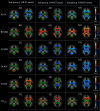
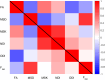
Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging (dMRI) is sensitive to white matter microstructural changes across the human lifespan. Several models have been proposed to provide more sensitive and specific metrics than those provided by the conventional Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) analysis. However, previous results using different metrics have led to contradictory conclusions regarding the effect of age on fibre demyelination and axonal loss in adults. Moreover, it remains unclear whether these metrics provide distinct information about the effects of age, for example, on different white-matter tracts. To address this, we analysed dMRI data from 651 adults approximately uniformly aged from 18 to 88 years in the Cambridge Centre for Ageing and Neuroscience (Cam-CAN) cohort, using six dMRI metrics: Fractional Anisotropy (FA) from standard DTI; Mean Signal Diffusion (MSD) and Mean Signal Kurtosis (MSK) from Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging (DKI) applied to directional averaged diffusion-weighted signals; and Neurite Density Index (NDI), Orientation Dispersion Index (ODI), and isotropic Free water volume fraction (Fiso) estimated from Neurite Orientation Dispersion and Density Imaging (NODDI). Averaging across white-matter regions-of-interest (ROIs), second-order polynomial fits revealed that MSD, MSK, and Fisoshowed the strongest effects of age, with significant quadratic components suggesting more rapid and sometimes inverted effects in old age. Analysing the data in different age subgroups revealed that some apparent discrepancies in previous studies may be explained by the use of cohorts with different age ranges. Factor analysis of the six metrics across all ROIs revealed three independent factors that can be associated to 1) tissue microscopic properties (e.g., differences in fibre density/myelin), 2) free-water contamination, and 3) tissue configuration complexity (e.g., crossing, dispersing, fanning fibres). While FA captures a combination of different factors, other dMRI metrics are strongly aligned to specific factors (NDI and MSK with Factor 1, Fisowith Factor 2, and ODI with Factor 3). To assess whether directional diffusion and kurtosis quantities provide additional information about the effects of age, further factor analyses were also performed, which showed that additional information about the effects of age may be present in radial and axial kurtosis estimates (but not standard axial and radial diffusivity). In summary, our study offers an explanation for previous discrepancies reported in dMRI ageing studies and provides further insights on the interpretation of different dMRI metrics in the context of white-matter microstructural properties.
Keywords: MRI; age; diffusion; modelling; white matter.
© 2023 Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Published under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no actual or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Complementary MR measures of white matter and their relation to cardiovascular health and cognition.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 7;15(1):28890. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13610-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40775500 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the microstructural transition at the gray matter-white matter interface: Implementation and demonstration of age-associated differences.Neuroimage. 2025 Feb 1;306:121019. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2025.121019. Epub 2025 Jan 12. Neuroimage. 2025. PMID: 39809374 Free PMC article.
-
Translating state-of-the-art spinal cord MRI techniques to clinical use: A systematic review of clinical studies utilizing DTI, MT, MWF, MRS, and fMRI.Neuroimage Clin. 2015 Dec 4;10:192-238. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.11.019. eCollection 2016. Neuroimage Clin. 2015. PMID: 26862478 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pulse Pressure Impairs Cognition via White Matter Disruption.Hypertension. 2025 Sep;82(9):1480-1491. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.124.24543. Epub 2025 Jul 10. Hypertension. 2025. PMID: 40636963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anania , V. , Collier , Q. , Veraart , J. , Buikema , A. E. , Vanhevel , F. , Billiet , T. , Jeurissen , B. , den Dekker , A. J. , & Sijbers , J. ( 2022. ). Improved diffusion parameter estimation by incorporating T2 relaxation properties into the DKI-FWE model . Neuroimage , 256 , 119219 . 10.1016/J.NEUROIMAGE.2022.119219 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arfanakis , K. , Wilson , R. S. , Barth , C. M. , Capuano , A. W. , Vasireddi , A. , Zhang , S. , Fleischman , D. A. , & Bennett , D. A. ( 2016. ). Cognitive activity, cognitive function, and brain diffusion characteristics in old age . Brain Imaging Behav , 10 , 455 – 463 . 10.1007/s11682-015-9405-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
