Morphometric Analysis of the Maxillary Sinus and Its Implications for Sinus Augmentation Surgery in an Eastern Indian Population
- PMID: 40799863
- PMCID: PMC12340660
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.87809
Morphometric Analysis of the Maxillary Sinus and Its Implications for Sinus Augmentation Surgery in an Eastern Indian Population
Abstract
Introduction Sinus augmentation surgery, also called sinus graft or lift, involves elevating the Schneiderian membrane in the posterior maxilla to enhance alveolar bone height by placing a bone graft or osteogenic materials. This procedure is commonly performed to support dental implants. This study evaluates the morphometry of the maxillary sinus across different age groups within the Eastern Indian population and its implications for sinus augmentation surgery. Methods We analysed 85 patients (55 males (64.7%) and 30 females (35.3%)) who underwent computed tomography scans, assessing key parameters such as residual bone height, lateral wall thickness, medial wall thickness, and the sinus angle. Data were summarised and presented as mean ± SD for continuous variables and frequencies for categorical data. Inferential tests were used to analyse the parameters, with a significance level of p<0.05. Results Our findings indicate that 56.47% (n=48) of patients had a residual bone height of ≤5 mm, necessitating sinus augmentation surgery before dental implantation. While lateral wall thickness was an important factor in selecting the appropriate surgical approach, with 16.67% (n=8) requiring the lateral window technique and 83.34% (n=40) better suited for the crestal approach, no significant gender differences were observed. However, the need for sinus augmentation surgery was more common in the 21-40 age group (p=0.008). Notably, left-side residual bone height was significantly lower than right-side residual bone height, indicating lateral asymmetry. Conclusion This study emphasizes the importance of maxillary sinus morphometry in optimizing sinus augmentation surgery techniques tailored to individual anatomical variations to improve surgical outcomes in the Eastern Indian population.
Keywords: lateral wall thickness; maxillary sinus; morphometry; residual bone height; sinus augmentation surgery.
Copyright © 2025, Sahoo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Institutional Ethics Committee of All Indian Institute of Medical Sciences issued approval T/IM-NF/Anatomy/23/180. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
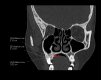
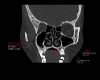
References
-
- Misch Misch, CE CE. Contemporary Implant Dentistry. Mosby; 2007.
-
- A literature review of the maxillary sinus with special emphasis on its anatomy and odontogenic diseases associated with it. Somayaji K, Muliya VS, Kg MR, Malladi UK, Nayak SB. Egypt J Otolaryngol. 2023;39:1–13.
-
- Bozhikova E, Uzunov N, Bozhikova E, Uzunov N. Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy and Conditions. IntechOpen; 2021. Morphological aspects of the maxillary sinus.
-
- The analysis of maxillary sinus aeration according to aging process; volume assessment by 3-dimensional reconstruction by high-resolutional CT scanning. Jun BC, Song SW, Park CS, Lee DH, Cho KJ, Cho JH. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005;132:429–434. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
