Research progress on the advantages, mechanisms and design strategies of nanomaterials for immunomodulatory angiogenesis
- PMID: 40799990
- PMCID: PMC12340402
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102147
Research progress on the advantages, mechanisms and design strategies of nanomaterials for immunomodulatory angiogenesis
Abstract
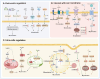
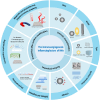
Owing to the difficulty in achieving effective and timely vascularization, repairing the structure and function of damaged tissues and organs remains a major challenge in clinical practice. The immune microenvironment is a key factor affecting angiogenesis; however, traditional strategies have failed to take full advantage of this property. Recent advances in nanomaterial design have shifted from "immune avoidance" to "immune interaction", representing a breakthrough in promoting angiogenesis. An increasing number of studies have reported that nanomaterials(NMs) can induce and regulate immune cells or immune metabolic reprogramming to promote angiogenesis, but few studies have investigated the specific mechanism by which NMs affect immune cells and how they are involved in different stages of angiogenesis. This article reviews the advantages of NMs and focuses on the specific mechanisms by which NMs regulate immune cells, including immune extracellular regulation (changes in the physical and chemical environment), the regulation of membrane receptors and membrane potential, and regulation within immune cells, such as the metabolic activity of immune cells. According to the application scenarios of tissue regeneration (bone, skin, nerve and cardiovascular tissue), the influencing factors and design smart nanomaterials through immune regulation are summarized, and the current challenges and development directions of NMs in clinical applications are proposed, particularly in precision medicine and clinical transformation. This review provides a theoretical basis for an in-depth understanding of NMs and immunomodulatory vascularization for tissue regeneration to optimize the design strategy, rational development and clinical application of NMs in the field of immunovascularization.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Immune metabolic reprogramming; Nanomaterials; Precision immunomodulation; Smart nanomaterials; Tissue regeneration.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
How to Implement Digital Clinical Consultations in UK Maternity Care: the ARM@DA Realist Review.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025 May;13(22):1-77. doi: 10.3310/WQFV7425. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025. PMID: 40417997 Review.
References
-
- Taraballi F., Sushnitha M., Tsao C., Bauza G., Liverani C., Shi A., Tasciotti E. Biomimetic tissue engineering: tuning the immune and inflammatory response to implantable biomaterials. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

