Allele-specific depletion of GNAQ Q209L via siRNA or an rAAV2-shRNA vector induces selective toxicity in GNAQ Q209L uveal melanoma cells
- PMID: 40800004
- PMCID: PMC12341522
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omton.2025.201020
Allele-specific depletion of GNAQ Q209L via siRNA or an rAAV2-shRNA vector induces selective toxicity in GNAQ Q209L uveal melanoma cells
Abstract
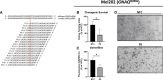
Approximately 80%-90% of uveal melanomas (UVM) harbor a single base pair substitution in one of two Gα protein subunits (GNAQ Q209L/P/GNA11 Q209L), resulting in constitutive activation and tumor initiation/progression. Herein, a small interfering RNA (siRNA) that specifically targets GNAQ Q209L transcripts induced significant cell death in GNAQ Q209L UVM cells, whereas little to no effects were observed on GNAQ wt cells or GNAQ wt transcripts. The most effective siRNA sequence was subsequently encoded into a short hairpin RNA (shRNA) cassette (shGNAQQ209L), expressed in a recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV), and the AAV2 capsid was selected for viral production upon completion of a serotype survey in UVM cells. Transduction with rAAV2-shGNAQQ209L induced significant cell death in GNAQ Q209L cells but not in a GNAQ wt UVM line. Unexpectedly, cell death in the GNAQ Q209L UVM cells was also observed upon transduction with the non-targeting control rAAV2 (although to a lesser degree than rAAV2-shGNAQQ209L), suggesting that an element of the AAV vector itself exhibits toxicity in GNAQ Q209L UVM cells. This work is among the first describing a genetic-based rAAV approach to specifically target an oncogenic mutant driver allele using single base pair allelic discrimination, collectively demonstrating that both siRNA and rAAV methods of GNAQ Q209L depletion result in significant UVM cell death.
Keywords: AAV; G-alpha-q; GNAQ; MT: Regular Issue; adeno-associated virus; cancer gene therapy; uveal melanoma.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T.F.M., M.L.H., and J.J.B. are co-inventors of presented technology and hold part ownership of submitted patent U.S. Provisional Application No. 63/650,097. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Inhibition of anti-apoptotic BCL2 overcomes adaptive resistance to co-targeting of the protein kinase FAK and MEK in GNAQ-driven uveal melanoma.J Biol Chem. 2025 Sep 11:110712. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110712. Online ahead of print. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40945724
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Cross talk between tumor stemness and microenvironment for prognosis and immunotherapy of uveal melanoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Oct;149(13):11951-11968. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05061-x. Epub 2023 Jul 7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37420017 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
